UNIT- 1
Introduction to E-commerce Tools
Ecommerce, additionally referred to as electronic commerce or web commerce, refers to the shopping for and mercantilism of products or services mistreatment the web, and also the transfer of cash and information to execute these transactions. Ecommerce is commonly wont to talk to the sale of physical product on-line, however it may also describe any reasonably business group action that's expedited through the web.
Whereas e-business refers to all or any aspects of operative a web business, ecommerce refers specifically to the group action of products and services.
The history of ecommerce begins with the primary ever on-line sale: on the August eleven, 1994 a person sold a CD by the band Sting to his friend through his web site NetMarket, Associate in Nursing yankee retail platform. this can be the primary example of a client getting a product from a business through the planet Wide Web—or “ecommerce” as we tend to unremarkably are aware of it nowadays.
Since then, ecommerce has evolved to form product easier to get and buy through on-line retailers and marketplaces. freelance freelancers, tiny businesses, and enormous companies have all benefited from ecommerce, that allows them to sell their merchandise and services at a scale that wasn't doable with ancient offline retail.
Types of Ecommerce Models
There are four main kinds of ecommerce models which will describe virtually each group action that takes place between shoppers and businesses.
1. Business to client (B2C):
When a business sells an honest or service to a private client (e.g. you purchase a combine of shoes from a web retailer).
2. Business to Business (B2B):
When a business sells an honest or service to a different business (e.g. A business sells software-as-a-service for alternative businesses to use)
3. client to client (C2C):
When a client sells an honest or service to a different client (e.g. You sell your previous article of furniture on eBay to a different consumer).
4. client to Business (C2B):
When a client sells their own product or services to a business or organization (e.g. Associate in Nursing influencer offers exposure to their on-line audience in exchange for a fee, or a creative person licenses their icon for a business to use).
Examples of Ecommerce
Ecommerce will defy a range of forms involving completely different transactional relationships between businesses and shoppers, likewise as completely different objects being changed as a part of these transactions.
1. Retail:
The sale of a product by a business on to a client with none mediator.
2. Wholesale:
The sale of product in bulk, typically to a distributer that then sells them on to shoppers.
3. Drop shipping:
The sale of a product, that is factory-made and shipped to the buyer by a 3rd party.
4. Crowd funding:
The collection of cash from shoppers ahead of a product being offered so as to lift the start-up capital necessary to bring it to promote.
5. Subscription:
The automatic revenant purchase of a product or service on an everyday basis till the subscriber chooses to cancel.
6. Physical products:
Any tangible sensible that needs inventory to be replenished and orders to be physically shipped to customers as sales are created.
7. Digital products:
Downloadable digital merchandise, templates, and courses, or media that has to be purchased for consumption or authorised to be used.
8. Services:
A ability or set of skills provided in exchange for compensation. The service provider’s time may be purchased for a fee.
Key takeaway
- Ecommerce, also known as electronic commerce or internet commerce, refers to the buying and selling of goods or services using the internet, and the transfer of money and data to execute these transactions. Ecommerce is often used to refer to the sale of physical products online, but it can also describe any kind of commercial transaction that is facilitated through the internet.
- Whereas e-business refers to all aspects of operating an online business, ecommerce refers specifically to the transaction of goods and services.
The Internet was launched in 1969 when the United States funded a project that developed a national computer network called Advanced Research Project
Agency Network (ARPANET). The Internet is a large network that connects together smaller networks all over the globe.
The Web was introduced in 1991 at the Center for European Nuclear Research (CERN) in Switzerland.
Prior to the Web, the Internet was all text—no graphics, animations, sound, or video. The Web made it possible to include these elements. It provided a multimedia interface to resources available on the Internet.
It is easy to get the Internet and the Web confused, but they are not the same thing. The Internet is the actual network. It is made up of wires, cables, satellites, and rules for exchanging information between computers connected to the network. Being connected to this network is often described as being online. The most common uses are the following:
Communicating is by far the most popular Internet activity. You can exchange e-mail with your family and friends almost anywhere in the world. You can join and listen to discussions and debates on a wide variety of special-interest topics.
Shopping is one of the fastest-growing Internet applications. You can window shop, look for the latest fashions, search for bargains, and make purchases.
Searching for information has never been more convenient. You can access some of the world’s largest libraries directly from your home computer.
You can find the latest local, national, and international news.
Education or e-learning is another rapidly emerging Web application. You can take classes on almost any subject. There are courses just for fun and there are courses for high school, college, and graduate school credit. Some cost nothing to take and others cost a lot.
Entertainment options are nearly endless. You can find music, movies, magazines, and computer games. You will find live concerts, movie previews, book clubs, and interactive live games.
Access
When provided with a connection to the Internet, you can use a browser program to search the Web.
Providers
The most common way to access the Internet is through an Internet service provider (ISP). The providers are already
connected to the Internet and provide a path or connection for individuals to access the Internet.
The most widely used commercial Internet service providers are national and wireless providers.
National service providers like Comcast, Qwest, and Verizon are the most widely used. They provide access through standard telephone or cable connections. Users can access the Internet from almost anywhere within the country for a standard fee without incurring long-distance telephone charges.
Wireless service providers offer Internet connections for computers with wireless modems and a wide array of wireless devices.
Browsers
Browsers are programs that provide access to Web resources. This software connects you to remote computers, opens and transfers files, displays text and images, and provides in one tool an uncomplicated interface to the Internet and Web documents.
Browsers allow you to explore, or to surf, the Web by easily moving from one Web site to another. Four well-known browsers are Mozilla Firefox, Apple Safari, Microsoft Internet Explorer, and Google Chrome.
For browsers to connect to resources, the location
or address of the resources must be specified. These addresses are called uniform resource locators (URLs). All URLs have at least two basic parts.
The first part presents the protocol used to connect to the
resource. Protocols are rules for exchanging data between computers. The protocol http is used for Web traffic and is
the most widely used Internet protocol. The second part presents the domain name. It indicates the specific address where the resource is located. The last part of the domain name following the dot (.) is the top-level domain (TLD). It identifies the type of organization.
Once the browser has connected to the Web site, a document file is sent back to your computer. This document typically
contains Hypertext Mark-up Language (HTML). The browser interprets the HTML formatting instructions and displays the document as a Web page.
Today it is common to access the Internet from a variety of mobile devices like cell phones. Special browsers called mobile browsers are designed to run on these portable devices.
Communication
Some popular types of Internet communication are e-mail, instant messaging, social networking, blogs, and wikis.
E-mail
E-mailer electronic mail is the transmission of electronic messages over the Internet. All you need to send and receive e-mail is an e-mail account, access to the Internet, and an e-mail program. Two of the most widely used e-mail programs are Microsoft’s Outlook Express and Mozilla Thunderbird.
A typical e-mail message has three basic elements: header, message, and signature. The header appears first and typically includes the following information:
Addresses: Addresses of the persons sending, receiving, and, optionally, anyone else who is to receive copies. E-mail addresses have two basic parts. The first part is the user’s name and the second part is the domain name, which includes the top-level domain.
Subject: A one-line description, used to present the topic of the message. Subject lines typically are displayed when a person checks his or her mailbox.
Attachments: Many e-mail programs allow you to attach files such as documents and image files. If a message has an attachment, the file name typically appears on the attachment line.
Unwelcome mail is called spam. While spam is indeed a distraction and nuisance, it also can be dangerous. For example,
computer viruses or destructive programs are often attached to unsolicited e-mail.
In an attempt to control spam, anti-spam laws have been added to our legal system. For example, CAN-SPAM requires that every marketing-related e-mail provide an opt-out option. When the option is selected, the recipient’s e-mail address is to be removed from future mailing lists. Failure to do so results in heavy fines. This approach, however, has had minimal impact since over 50 percent of all spam originates from servers outside the United States. A
more effective approach has been the development and use of spam blockers, also known as spam filters. These programs use a variety of different approaches to identify and eliminate spam.
InstantMessaging
Instant messaging (IM) allows two or more people to contact each other via direct, live communication. To use instant messaging, you register with an instant messaging server and
then specify a list of friends.
The most widely used instant messaging services are AOL’s
Instant Messenger, Microsoft’s MSN Messenger, and Yahoo Messenger. One limitation, however, is that many instant messaging services do not support communication with other services. For example, at the time of this writing, a user registered with AOL cannot use AOL’s Instant Messenger software to communicate with a user registered with Yahoo Messenger. Recently, however, some software companies have started providing universal instant messenger programs that overcome
this limitation. Three widely used programs are Digsby, Pidgin, and Qnext.
SocialNetworking
Reuniting sites are designed to connect people who have known one another but have lost touch; for example, an old high school friend that you have not seen for several years. You join a social network by connecting to a reuniting site and providing profile information such as your age, gender, name of high school, and so forth. This information is added to the reuniting site’s member database. Members are able to search the database to locate individuals. Two of the best-know reuniting sites are Classmates Online and Facebook.
Friend-of-a-friend sites are designed to bring together two people who do not know one another but share a common friend. The theory is that, if you share a common friend, then it is likely that you would become friends. For example, a network could be started by one of your acquaintances by providing profile information on him- or herself and a list of friends. You could visit your acquaintance’s site to connect to a friend(s) of your acquaintance. You could even join the list of friends provided at the
site. Two well-known friend-of-a-friend sites are Friendster and MySpace.
Common interest sites bring together individuals that share common interests or hobbies. You select a networking site based on a particular interest. For example, if you wanted to share images, you might join Flickr or YouTube. If you are looking for business contacts, you might join Linkedln. If you wanted to locate or create a special interest group, you might join Meetup.
Blogs,Microblogs,andWikis
In addition to social networking sites, there are other types of sites
that help ordinary people communicate across the Web.
Many individuals create personal Web sites, called Web logs or
blogs, to keep in touch with friends and family. Blog postings
are timestamped and arranged with the newest item first. Often, readers of these sites are allowed to comment. Some blogs are like online diaries with personal information; others focus on information about a hobby or theme, such as knitting, electronic devices, or good books. Although most are written by individual bloggers, there are also group blogs with multiple contributors. Some businesses and newspapers also have started blogging
as a quick publishing method. Several sites provide tools to create blogs. Two of the most widely used are Blogger and WordPress.
A microblog publishes short sentences that only take a few seconds to write, rather than long stories or posts like a traditional blog. Microblogs are designed to keep friends and other contacts up-to-date on your interests and activities. The most popular microblogging site, Twitter, enables you to add new content from your browser, instant messaging application, or even a mobile phone. To learn more about Twitter, see Making IT Work for You: Twitter on pages 40 and 41.
A wiki is a Web site specially designed to allow visitors to fill in missing information or correct inaccuracies. “Wiki” comes from the Hawaiian word for fast, which describes the simplicity of editing and publishing through wiki software. Wikis support collaborative writing in which there isn’t a single expert author, but rather a community of interested people that builds knowledge over time. Perhaps the most famous example is Wikipedia, an online encyclopedia, written and edited by anyone who wants to contribute, that has millions of entries in over 20 languages.
SearchTools
A number of organizations called search services operate Web sites that can help you locate the information you need. Special programs called spiders continually look for new information and update the search services’ databases. Additionally, search services provide special programs called search engines that you can use to locate specific information on the Web.
SearchEngines
Search engines are specialized programs that assist you in locating information on the Web and the Internet. There are search approaches:
Keyword search: In a keyword search, you enter a keyword or phrase reflecting the information you want. The search engine compares your entry against its database and returns a list of hits, or sites that contain the keywords. Each hit includes a hyperlink to the referenced Web page (or other resource) along with a brief discussion of the information contained at that location. Many searches result in a large number of hits. For example, if you were to enter the keyword travel, you would get thousands of hits. Search engines order the hits according to those sites that most likely contain the information requested and present the list to you in that order, usually in groups of 10.
Directory search: Most search engines also provide a directory or list of categories or topics such as Autos, Finance, and Games. In a directory search, you select a category or topic that fits the information that you want. Another list of subtopics related to the topic you selected appears. You select the subtopic that best relates to your topic and another subtopic list appears. You continue to narrow your search in this manner until a list of Web sites appears. This list corresponds to the hit list previously discussed.
MetasearchEngines
Metasearch engines are programs that automatically submit your
search request to several search engines simultaneously. The metasearch engine receives the results, eliminates duplicates, orders the hits, and then provides the edited list to you.
SpecializedSearchEngines
Specialized search engines focus on subject-specific Web sites. Specialized sites can potentially save you time by narrowing
your search.
ElectronicCommerce
Electronic commerce, also known as e-commerce, is the buying and selling of goods over the Internet. There are three basic types of electronic commerce:
Business-to-consumer (B2C) involves the sale of a product or service to the general public or end users. Oftentimes this arrangement eliminates the wholesaler by allowing manufacturers to sell directly to customers. Other times, existing retail stores use B2C e-commerce to create a presence on the Web as another way to reach customers. The three most widely used B2C applications are for online banking, financial trading, and shopping.
Online banking is becoming a standard feature of banking institutions. Customers are able to go online with a standard browser to perform many banking operations. These online operations include accessing account information, balancing check books, transferring funds, paying bills, and applying for loans.
Online stock trading allows investors to research, buy, and sell stocks and bonds over the Internet. While e-trading is more convenient than using a traditional full-service broker, the greatest advantage is cost.
Online shopping includes the buying and selling of a wide range of consumer goods over the Internet. There are thousands of e-commerce applications in this area.
Consumer-to-consumer (C2C) involves individuals selling to individuals. This often takes the form of an electronic version of the classified ads or an auction.
Web auctions are similar to traditional auctions except that buyers and sellers seldom, if ever, meet face-to-face.
Business-to-business (B2B) involves the sale of a product or service from one business to another. This is typically a manufacturer–supplier relationship.
Plug-ins
Plug-insare automatically loaded and operate as part of a browser. Many Web sites require specific plug-ins to fully experience their content. Some plug-ins are included in many of today’s browsers; others must be installed.
Filters- Filters are used by parents and organizations to block certain sites and to monitor use of the Internet and the Web.
- File Transfer Utilities
File transfer utilities copy files to ( downloading ) and from (uploading) your computer. Three types are - File transfer protocol (FTP) and secure file transfer protocol (SFTP) allow you to efficiently copy files across the Internet.
- Web-based file transfer services make use of a Web browser to upload and download files.
BitTorrent distributes file transfers across many different computers.
Internet Security Suite - An Internet security suite is a collection of utility programs designed to protect your privacy and security on the Internet.
Key takeaway
- Electronic commerce, also known as e-commerce, is the buying and selling of goods over the Internet. There are three basic types of electronic commerce:
Business-to-consumer (B2C) involves the sale of a product or service to the general public or end users. Oftentimes this arrangement eliminates the wholesaler by allowing manufacturers to sell directly to customers. Other times, existing retail stores use B2C e-commerce to create a presence on the Web as another way to reach customers. The three most widely used B2C applications are for online banking, financial trading, and shopping.
There is rarely a facet within an industry that hasn’t been touched by technology. Most notably, big data and machine learning are paving the way for robotics automation, the instant transfer of data, and a variety of interesting devices.
The retail industry is no exception when it comes to taking advantage of technology. In fact, successful businesses are setting the bar by implementing technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), chatbots, and voice assistants into their operations. The reasons vary, but can include that these technologies help provide excellent customer experiences through instant communication, providing support without the help of live employees, data management and security, and much more.
Many online stores already have integrated e-commerce software, but to stay in the competition, any e-commerce business must give serious thought into the following technologies to stay prosperous and maintain customer satisfaction.
AI is revealing valuable insights into customer preferences — which can guide marketing campaigns. It also can provide for the automation and transfer of data management operations to increase performance. In the retail and e-commerce world, AI is being relied upon for several unique aspects of business.
74% of businesses believe that user experience is important for improving sales and conversions. AI provides a personalized user experience that 59% of customers say influences their shopping decisions. Artificial intelligence can facilitate a shopping experience that is supported by customers’ personal preferences.
AI, big data, and machine learning can offer analytics and foresight into customer behavior patterns which can drive advertising campaigns, provide support and services, and automate communication — all of which increase engagement rates for businesses.
Since AI can predict customer behavior patterns, it is able to recommend relevant and useful information to customers on products and services and more. AI and machine learning algorithms can efficiently forecast this information by taking in a customer’s search history and other third-party data. This can lead to effectively proposing applicable information and solutions to satisfy customer needs.
Customer behavior patterns are a driving force behind any marketing campaign. Using AI, businesses are able to target both potential and existing customers by looking at data such as past certain history. These analytics can be used to provide a better aimed content marketing strategy for businesses.
Content and advertisements may then be created with a tone that engages various audiences and placed on the correct media platform to capture their attention. Using AI and marketing automation can show a business the data necessary for a strategic and tactical campaign.
You will be hard-pressed to find a successful business that does not have at least one aspect of their business operations posted on the cloud. Managing and processing data in the cloud is essential for the instant access of data by anyone who needs it, on any device. Especially for e-commerce businesses, a cloud ERP can improve delivery speeds, make your store more adaptable, and bring about business stability and growth.
Recognized for their customer satisfaction rates and wide-scale availability, chatbots have pivoted from limited use in call centers to wide-spread e-commerce website applications. Rather than asking questions and providing information to those over the phone, e-commerce websites that utilize chatbots can provide a variety of services and solutions.
Many businesses cannot provide answers exactly when a potential customer is searching for them. Additionally, customers may be frustrated when put on hold because a business does not have the staff to answer and tend to a high volume of customers.
Chatbots are available 24/7, day and night, to provide any answers and solutions a potential customer may inquire about. Having this automated communication can be valuable for businesses as it frees up employees to focus on other business operations, efficiently communicates with customers, and may even propose products and services.
Built into a chatbot’s algorithm is what is called a decision tree. Decision trees use machine and deep learning to automate complex business processes, essentially developing, maintaining, and always expanding upon a comprehensive network of if/then statements.
By addressing commonly asked questions and concerns from customers, chatbots are able to expand upon their decision tree. Here, a chatbot can gain information on whether they’ve helped a customer or not. If they have helped the customer, this information may be passed on to another consumer with a similar question. If they have not adequately satisfied the customer, the chatbot may continue asking questions until they provide the customer with the information they are looking for. When they have answered the customer, the chatbot now has more choices in their decision tree to help customers in the future.
Send shipping and tracking information
Imagine if Amazon never remembered your address or payment information and never told you when your order is scheduled to arrive. It is a pain for customers to have to enter shipping information every time they want to order something from your e-commerce website. Additionally, it is a best practice for user experience to give a customer a timeframe for when the order will be at their doorstep.
Chatbots remember this information and can provide real-time shipping tracking details for customers. This can also help warehouse operations, as they could focus on the supply chain and fulfilling orders through their order management system rather than telling customers where their packages are.
Not everyone searches for products and information via mouse and keyboard in the digital age. To accommodate these potential customers, businesses will need to adopt voice commerce — using voice recognition technology and allowing customers to use voice commands to find and purchase products online. Voice assistants such as Siri, the Amazon Echo, and Google Home are becoming increasingly popular for their convenience in searching for and purchasing products. In order to stay successful, e-commerce businesses will need to provide this technology and its benefits to capture a new wave of consumers.
Any company jingle, music composition, or auditory tone is considered an audio brand signature. It is a way for businesses to better establish a brand identity, and help customers remember their name.
Businesses can command their audio brand signature to play through voice assistants to let their customers know where they are ordering their products from. By associating your brand with an auditory signature, consumers will know and remember they are ordering from your store – even when laying on their couch, speaking to a voice assistant.
Customers would rather automate their continual shopping needs than frequent a website (or store) every month for their essentials. Through voice assistants, people are able to compile shopping lists — ordering what they need from who they want. This technology learns the preferences of the owners, and many businesses are able to capitalize on brand loyalty. If a voice assistant knows that a person wants a product from your store monthly, it can add it to their shopping list. This can be beneficial to companies in forecasting sales and balancing order management.
In the marketing world, assistive technology and voice commerce are helping to reach a wide variety of new audiences — not just the younger generation who are using new devices, but the visually impaired as well. By using speech-to-text technology, the visually impaired can forgo the struggles of traditional search experience, and order what they need through new and developing assistive technology.
All interconnected, AI, chatbots, and voice assistants are becoming necessary for any e-commerce business to be successful. In order to stay with the times, businesses must adapt to these new technologies which appeal better to potential and existing customers.
Discover more B2B e-commerce trends and stats
- Get to know your customers: download our B2B Buying Process 2019 Report for stats and insights into the behavior, preferences and challenges of buyers, based on a survey of 500+ B2B customers.
- Discover the e-commerce trend toward B2B2C and D2C sales, including what other businesses are doing, and how you can respond.
- See how e-commerce trends have evolved and how to get ready for the future of e-commerce with our B2B e-commerce trends timeline.
- Understand the business benefits of ERP-integrated e-commerce based on a survey of global B2B and B2C customers.
Key takeaway
- There is rarely a facet within an industry that hasn’t been touched by technology. Most notably, big data and machine learning are paving the way for robotics automation, the instant transfer of data, and a variety of interesting devices.
- The retail industry is no exception when it comes to taking advantage of technology. In fact, successful businesses are setting the bar by implementing technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), chatbots, and voice assistants into their operations.
- The reasons vary, but can include that these technologies help provide excellent customer experiences through instant communication, providing support without the help of live employees, data management and security, and much more.
- Online shopping for retail sales direct to consumers via Web sites and mobile apps, and conversational commerce via live chat, chatbots, and voice assistants
- Providing or participating in online marketplaces, which process third-party business-to-consumer or consumer-to-consumer sales
- Business-to-business buying and selling;
- Gathering and using demographic data through web contacts and social media
- Business-to-business (B2B) electronic data interchange
- Marketing to prospective and established customers by e-mail or fax (for example, with newsletters)
- Engaging in pretail for launching new products and services
- Online financial exchanges for currency exchanges or trading purposes.
Key takeaway
- Online shopping for retail sales direct to consumers via Web sites and mobile apps, and conversational commerce via live chat, chatbots, and voice assistants
- Providing or participating in online marketplaces, which process third-party business-to-consumer or consumer-to-consumer sales
- Business-to-business buying and selling;
- Gathering and using demographic data through web contacts and social media
Four Traditional Types of Ecommerce Business Models
If you’re starting an ecommerce business, odds are you’ll fall into at least one of these four general categories.
Each has its benefits and challenges, and many companies operate in several of these categories simultaneously.
Knowing what bucket your big idea fits in will help you think creatively about what your opportunities and threats might be.
1. B2C – Business to consumer.
B2C businesses sell to their end-user. The B2C model is the most common business model, so there are many unique approaches under this umbrella.
Anything you buy in an online store as a consumer — think wardrobe, household supplies, entertainment — is done as part of a B2C transaction.
The decision-making process for a B2C purchase is much shorter than a business-to- business (B2B) purchase, especially for items that have a lower value.
Think about it: it’s much easier for you to decide on a new pair of tennis shoes than for your company to vet and purchase a new email service provider or food caterer.
Because of this shorter sales cycle, B2C businesses typically spend less marketing dollars to make a sale, but also have a lower average order value and less recurring orders than their B2B counterparts.
And B2C doesn’t only include products, but services as well.
B2C innovators have leveraged technology like mobile apps, native advertising and remarketing to market directly to their customers and make their lives easier in the process.
For example, using an app like Lawn Guru allows consumers to easily connect with local lawn mowing services, garden and patio specialists, or snow removal experts.
Additionally, home service businesses can use Housecall Pro’s plumbing software app to track employee routes, text customers, and process credit card payments on the go, benefitting both the consumer and business alike.
2. B2B – Business to business.
In a B2B business model, a business sells its product or service to another business. Sometimes the buyer is the end user, but often the buyer resells to the consumer.
B2B transactions generally have a longer sales cycle, but higher order value and more recurring purchases.
Recent B2B innovators have made a place for themselves by replacing catalogs and order sheets with ecommerce storefronts and improved targeting in niche markets.
In 2020, close to half of B2B buyers are millennials — nearly double the amount from 2012. As younger generations enter the age of making business transactions, B2B selling in the online space is becoming more important.
3. C2B – Consumer to business.
C2B businesses allow individuals to sell goods and services to companies.
In this ecommerce model, a site might allow customers to post the work they want to be completed and have businesses bid for the opportunity. Affiliate marketing services would also be considered C2B.
Elance (now Upwork) was an early innovator in this model by helping businesses hire freelancers.
The C2B ecommerce model’s competitive edge is in pricing for goods and services.
This approach gives consumers the power to name their price or have businesses directly compete to meet their needs.
Recent innovators have creatively used this model to connect companies to social media influencers to market their products.
4. C2C – Consumer to consumer.
A C2C business — also called an online marketplace — connects consumers to exchange goods and services and typically make their money by charging transaction or listing fees.
Online businesses like Craigslist and eBay pioneered this model in the early days of the internet.
C2C businesses benefit from self-propelled growth by motivated buyers and sellers, but face a key challenge in quality control and technology maintenance.
Five Value Delivery Methods for Ecommerce Innovation
If your business model is the car, then your value delivery method is the engine.
This is the fun part — where you find your edge. How will you compete and create an ecommerce business worth sharing?
Here are a few of the popular approaches taken by industry-leaders and market disruptors.
By cutting out the middleman, a new generation of consumer brands have built loyal followings with rapid growth.
Online retailers like Warby Parker and Casper set the standard for vertical disruption, but brands like Glossier are showing us how D2C can continue to be an area for innovation and growth.
2. White label and private label.
To “white label” is to apply your name and brand to a generic product purchased from a distributor.
In private labeling, a retailer hires a manufacturer to create a unique product for them to sell exclusively. With private labeling and white labeling, you can stay lean on your investments in design and production and look for an edge in technology and marketing.
In a wholesaling approach, a retailer offers its product in bulk at a discount.
Wholesaling is traditionally a B2B practice, but many retailers have offered it to budget-conscious consumers in a B2C context.
One of the fastest growing methods of ecommerce is dropshipping.
Typically, dropshippers market and sell items fulfilled by a third party supplier, like AliExpress or Printful. Dropshippers act as a middle man by connecting buyers to manufacturers. Easy-to-use tools allow BigCommerce users to integrate inventory from suppliers around the world for their storefronts.
As early as the 1600s, publishing companies in England used a subscription model to deliver books monthly to their loyal customers. With ecommerce, businesses are going beyond periodicals and fruit of the month clubs. Today, virtually every industry has seen the arrival of subscription services to bring convenience and savings to customers.
5 Examples of Innovative Ecommerce Business Plans
Many companies have flourished with the freedom ecommerce gives them. These brands have combined classic business models with something new, making them innovative leaders in the field.
In 2018, LARQ launched the first self-cleaning water bottle. This reusable, rechargeable bottle uses UV-C technology to eliminate viruses and bacteria in water, whether it’s from a tap or a natural source.
LARQ’s launch was the largest crowdfunded effort for a clean water initiative with $1.7 million raised. Today, LARQ donates 1%of its proceeds to efforts for clean drinking water around the world.
Buyers were attracted to this reusable bottle because of its eco-friendly factors, while they can also save money skipping on single-use water bottles, but still enjoy a clean water vessel (without scrubbing it) every time. These unique factors have led to LARQ’s increased revenue by 400% year-over-year.
2. Beer Cartel – Subscription service.
Some ideas sell themselves.
Beer Cartel offers Australia’s longest running beer subscription service, with expert-selected craft beers from around the globe delivered to subscribers’ doorsteps each month.
They’ve attracted the curious and the connoisseurs by giving their customers a unique selection at a price better than what they could get in stores.
Beer Cartel has also done a great job of offering several different subscription options to serve customers of all appetites and budgets.
Fortune 500 companies an family-owned startups alike trust Berlin Packaging for sourcing, designing, and distributing their containers and closures. As a hybrid supplier, Berlin Packaging brings their expertise to every level of the supply chain to increase efficiency and lower cost for their customers.
Berlin Packaging is over 80 years old but has kept their advantage by innovating every step of the way. By adopting an ecommerce business model, they stayed competitive by making it easy for their customers to shop from their large selection of containers sourced from more than 200 different partner vendors. Berlin Packaging also prioritized a strong connection between their site and ERP, making it easier for customers to see their credit limits, balances, and past due balances.
Atlanta Light Bulbs is no stranger to innovative ecommerce. ALB launched their first ecommerce site in 1999, which gave them a huge head start on creating a unique site experience for their customers.
As their market has shifted to the millennial generation, Atlanta Light Bulbs has focused on adding more to their online platform that will set them apart from their competition, such as using apps for their BigCommerce storefront.
Their mobile shopping app has primarily helped grow Atlanta Light Bulbs’ B2C sales, but even their commercial clients have come to enjoy the convenience of ordering from their mobile devices.
Another creative tactic from ALB is their make an offer feature, which allows buyers to name a quantity and price and submit an offer. On the backend, pricing rules are used to auto-calculate the lowest price Atlanta Light Bulbs can give. Customers receive a message letting them know their proposal has been accepted and they can checkout, or, if the price is too low, a different deal is offered.
5. Mountain Crest Gardens – Wholesaling.
Mountain Crest Gardens began as a family-owned and operated business in Northern California in the mid-90s. But when they relaunched their website in 2012, they saw 10x the revenue and a 400% increase in orders.
Mountain Crest Gardens capitalized on what made them unique: their aesthetically beautiful succulents. User-generated content organically amplifies the plants and drives orders. Plus, Mountain Crest Gardens caters to different consumers as they offer individual succulents, wholesale options and even a subscription box.
Selecting Your Ecommerce Business Model
We’ve talked about your broader options for choosing an ecommerce business model, now let’s look at the specifics.
Here are a few questions that will help you create a plan that will set your company apart.
The key here is honesty and research.
Spend time learning about the market you’re targeting and be honest about what unique value you can bring to the space.
Who are you looking to serve?
Consider what their expectations are when purchasing the type of product you plan to sell.
You’re most likely to succeed if you can understand their behaviors and habits and find ways to improve them or save money.
To do this, you’ll need to look for pain points in the way things are currently done.
This is where you as an innovator can carve a space for yourself.
What do you know better than anyone else?
Build around your existing strengths and the pieces that are energizing to you.
Be realistic about what elements you can do yourself and what you will need to find help for.
It can be challenging to know your limitations but it will help you make better long-term decisions.
3. What is best for your product?
Depending on your product, different models will serve you better than others.
For example, if you are manufacturing your own products, you may want to consider wholesaling or subscriptions to help cover production costs and break even more quickly.
If you are a distributor of other people’s products, you’ll want to invest more heavily into direct marketing and strategies that will grow your customer base.
You understand what makes your product better, but will consumers?
Evaluate your competition and make sure it’s clear why your product is the best choice.
Are you competing on price? Selection?Convenience?
From your back end processes, to your warehousing, to your marketing, to your website’s shopping experience, your unique value should be clear.
We’ve covered the most common ecommerce business models, several tactics for ecommerce innovation, and examples of ecommerce businesses that have blazed their own path.
We’ve talked about the questions you’ll need to answer to find a niche where your new endeavor can thrive.
Planning is important, but innovation doesn’t happen in a vacuum. It’s time to get your solution out into the world and begin to refine your business based on the feedback you receive.
Key takeaway
- If you’re starting an ecommerce business, odds are you’ll fall into at least one of these four general categories.
- Each has its benefits and challenges, and many companies operate in several of these categories simultaneously.
- Knowing what bucket your big idea fits in will help you think creatively about what your opportunities and threats might be.
The availability and continued growth of Internet technologies (IT) have created great opportunities for users all over the globe to benefit from IT services and use them in a variety of different ways. The use of IT to conduct business online is known as Electronic Commerce (E-Commerce).
We are witnessing a boom of new technologies, especially in the service sector (IT, Telecommunications, Internet, etc.). Due to technological advances economic transactions have become much easier and faster and this is mainly because of the development of e-commerce. Real engine of the new economy, e-commerce is a remarkable source of competitive advantage for businesses and a new space for consumers. In the coming years, growth and profitability will depend most likely the ability to introduce these new emerging technologies and adopt new methods of business transactions. Since many years ago computers, appliances, plane tickets and many other items are available for purchase on the Internet using cards issued by local banks. Although this technological trend could significantly strengthen the national economic structure, its role and place in developing countries economic structure remains unclear and leaves many questions to ask:
Where is the e-commerce today?
What are the obstacles to e-commerce? Is e-commerce having a bright future to become a mainstream business for growth, and what steps to take to get there?
While developed countries have harnessed and adopted E-Commerce, developing countries are not yet fully adapted to its adoption. The aim of this study is to investigate the factors that play a role in the adoption and development of E-Commerce and, hence, develop strategies that conceptualize the influential factors that form as enablers and disablers of E-Commerce. In this paper we provide some answers about the current situation of e-commerce think later on prospects that will enable the benefits from all the advantages offered by this new mode of trade. This paper is organized as follows. Firstly, a concept of e-commerce is briefly introduced, followed by the construction of the research model, including all the aspects of e-commerce that are the object of our investigation. Finally, implications drawn on the study results and analysis are discussed, followed by the research limitations and a conclusion.
2. Understanding the Concept of E-Commerce
Information and communication technology (ICT) is radically transforming the way individuals, organizations, and governments work. The internet in today’s information societies has become an essential channel that is used for dissemination of information, products, and services. People prefer to use the internet as a transaction tool in different areas, such as, learning, shopping, marketing, travel, trading, etc. Carter and Belanger (2003) emphasized the use of ICT to improve efficiency and access to government services across all stakeholders in G2C, G2E, G2G and G2B services. Additionally, governments have realized the importance of the internet and have undertaken critical transformations to use it to deliver public services, so that citizens can always access them regardless of their location (Abdulkarim, 2003). Fang (2002) has described e-government (part of e-commerce) as a method for governments to use the most innovative ICT services, particularly web-based internet applications. These applications are able to provide citizens and businesses with more convenient access to government information and services, to improve the quality of services and provide more opportunities for democratic institutions and processes. E-Commerce involves many issues such as trust, security, privacy, accessibility, familiarity, awareness, and quality of public services (Jaeger, 2003).
For instance, the rapid growth of E-Commerce initiatives in the MENA (Middle East and North Africa) region reflects its compelling advantages, such as enhanced governmental performance, lower cost structure, greater flexibility, broader scale and scope of services, greater transparency, accountability, and faster transactions. However, getting people to be continually engaged in e-commerce services is a challenge since only with a few mouse clicks they will be moved away. An agreement seems to enhance better customer service and its consequent effect on online satisfaction and reuse. Especially, online satisfaction is not the only primary driver of online customers’ continuous behavior, but also the key to building and retaining a loyal base of long-term customers. Many institutions, such as the World Bank, the United Nations, Europe’s Information Society DG, the Canadian Common Measurement Tool (CMT) of satisfaction, the European Customer Satisfaction Index and the American Customer Satisfaction Index, evaluate e-commerce progress and satisfaction using various methods and indices (Fitsilis, Anthopoulos, &Gerogiannis, 2010). factors influencing e-commerce
Businesses implementing E-Commerce in developing countries face substantially greater challenges than businesses in developed countries due to the unreliability of the internet connection, the poor availability of accessing it due to the poor infrastructure, the high cost of doing so, and also the low level of ICT penetration throughout the country (Molla and Licker, 2005b; Molla and Licker, 2005a). Aleid (2009) carried out an investigation of different E-Commerce schemes in a number of countries with regard to culture, infrastructure and human behavior. They find that there are a number of factors that may inhibit the diffusion of E-Commerce into developing countries (e.g. infrastructure, security, E-Commerce laws). This study will focus on Developing countries, which is considered to be a marketplace, which is booming for E-Commerce activities in the Middle East (Eid, 2011). Developing countries require further Internet access, exploring opportunities for the Internet in education, government and commerce. However, for these things to be achieved certain requirements need to exist where certain factors play an important role. Next we discuss the most essential factors for the development and effectiveness of e-commerce. factors influencing e-commerce
3. Key Factors Impacting Ecommerce
Johnson-George and Swap (1982: 1306) asserted that “willingness to take risks may be one of the few characteristics common to all trust situations.” Kee and Knox (1970) argued that to appropriately study trust there must be some meaningful incentives at stake and that the trustor must be cognizant of the risk involved. The definition of trust proposed in this research is the willingness of a party to be vulnerable to the actions of another party based on the expectation that the other will perform a particular action important to the trustor, irrespective of the ability to monitor or control that other party (Park and Kim, 2003). Trust can be a vital factor in business to consumer (B2C) E-Commerce. It gives consumers faith to buy products or services even if an e-trader is unknown. It encourages more use of E-Commerce technologies, makes the e-transaction process easier, enhances the level of acceptance and adoption of E-Commerce, leads to the improvement of consumer commitment, raise customer satisfaction, introduces the concept of loyalty, sustains long-term relationships with customers and assists the acquiring of a competitive benefit. Future purchases can be motivated and increased prices tolerated. It reduces customer worries about information privacy, and helps customers to tolerate the irregular mistakes made by the e-trader (Pittayachawan, 2008). Trust is a complicated concept and has a multitude of sides to be addressed. There are a number of researchers who have continually approached the ‘trust’ issue from a technical side such as Internet and network security and even web interface design (Fernandes, 2001; Clifford et al., 1998; Pittayachawan, 2008). Nonetheless, according to Klang (2001) and Ratnasingham and Kumar (2000), considering just the technical perceptions will not guarantee trust in e-commerce.
It is widely acknowledged by both government and industrial organizations that, from a consumer point of view, issues of information security are a major obstacle to the growth of E-Commerce. The perception of risk regarding Internet security has also been recognized as a concern for both experienced and inexperienced users of Internet technologies (Miyazaki and Fernandez, 2001). Furthermore, Miyazaki and Fernandez (2001) have identified the fraudulent behavior by online retailers as a key concern for Internet users and, therefore, E-Commerce users Rose et al. (1999) identifies hackers as an obvious security threat to E-Commerce.
This happens because the online availability and accessibility of the stored data of many corporations gives any hacker on the Internet the chance to steal data from these corporate databases. These threats have been identified in several new studies (Aleid et al., 2009; Al-Ghaith et al., 2010). Dixit and Datta (2010) studied the acceptance of e-banking among adult customers in India. The findings depicted that many factors like security and privacy, trust, innovativeness, familiarity, and awareness level increase the acceptance of e-banking services among Indian customers.
Awareness and Perceived Usefulness
Within the context of the information systems (IS) domain, much research has outlined the significance of the influence of perceived usefulness on attitude towards the use of e-commerce.
The real reason why customers would use E-Commerce is that they find it a useful facility for conducting shopping online (Alghamdi, 2011). Furthermore, according to Sathye’s (1999) research, the use of online banking services, which is a good example of e-commerce, is new knowledge to many customers, and the lack of awareness of online banking is a crucial factor in preventing customers from adopting it. In his study of 500 Australian customers, he concluded that customers were not aware of the potential benefits of online banking. This was supported by another study by Howcroft et al., (2002) in which they found that the issue of lack of awareness and knowledge of online banking services contributes e-commerce adoption challenges. Suki and Ramayah (2010) studied user acceptance of the e-Government services in Malaysia. Their results indicate that the important determinants of user acceptance of the e-Government services are perceived usefulness, ease of use, compatibility, interpersonal influence, external influence, self-efficacy, facilitating conditions, attitude, subjective norms, perceived behavioral control, and intention to use e-Government services/system.
As the internet is fast becoming a major source of information and services, a well-designed e-commerce website has become essential so that citizens can access public information and improve their participation. E-commerce websites can serve as a tool for both communication and relations for the customers and general public. Information and data can easily be shared with and transferred to external stakeholder (Moon, 2002). Henry (2006) defines web accessibility as getting people to use, perceive, understand, direct and interact with the web. The International Standards Organizations (ISO) has defined accessibility as “the usability of a product, service, environment or facility by people with the widest range of capabilities”.
Gummerus et al. (2004) define the user interface as the channel through which customers are in contact with the e-service provider. Park and Kim (2003) found that the quality of the user interface affects customer satisfaction directly, since it provides physical evidence of the service provider’s competence as well as facilitating effortless use of the service. Because of its importance to customer satisfaction, Tan, Tung, and Xu (2009) identified fourteen key factors for developing effective B2C e-commerce websites. Also, Cyr (2008) investigated the effect of B2C e-commerce website user interface design factors (such as information design, navigation design, and visual design) on trust and satisfaction across three developed countries; Canada, Germany, and China. Cyr found that these user interface design variables are key antecedents to website trust and website satisfaction across cultures.
The perceived quality of a service has two dimensions; the technological dimension, which refers to what is delivered, and the functional dimension, which refers to how the service is delivered. Speed of response, offer updates, and site effectiveness, refers to the technical quality (Rust & Lemon, 2009). Interactive communication, personalization of the communication and of the service, as well as new forms of customer access refers to the functional aspect of quality. Product/service quality is defined as the customer perception of the quality of information about the product/service that is provided by a website (Park & Kim, 2003). According to Mcknightetal., 2002, website content quality has been argued to be an antecedent of online customer trust on quality. In addition, Park and Kim (2003) found that the information quality affects customer satisfaction directly. Karunasena and Deng (2012) have identified the critical factors for evaluating the public value of e-Government in Sri Lanka. The study showed that the deliveries of quality information and services, user-orientation of information and services, efficiency and responsiveness of public organizations and contributions of public organizations to the environmental sustainability are the critical factors for evaluating the public value of e-Government in Sri Lanka.
The government’s role in developing countries as an important one that facilitates the essential requirements for the development of E-Commerce such as providing robust secure online payment options, ensuring a solid ICT infrastructure, providing educational programs and building up awareness using different means such as media and education institutions. The results of their study show the significance of government promotion and support as a crucial factor (AlGhamdi et al., 2011). According to Molla and Licker (2005), state that the government demonstrates strong commitment to promoting E-Commerce. In Saudi Arabia, Eid (2011) posit in his study that the Saudi Government’s support was recognized as an important element in the development and growth of local E-Commerce. According to Eid’s study, some Saudi citizens believe in the importance of the government’s role. Interviewee 8 commented on the diffusion of E-Commerce by government and private accreditation in providing the basic facilities such as a house address for every citizen, to be used online for accurate delivery of products and documents and special services. If there is no reliable postal service, there will be no e-government. factors influencing e-commerce
4. Constructing a Research Model
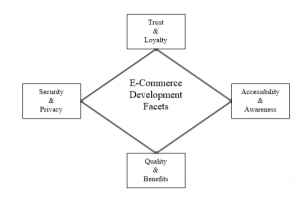
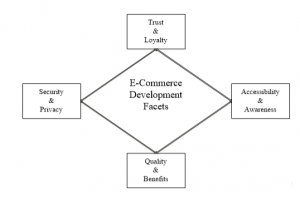
The development of E-Commerce in this research is measured along the four facets stipulated in the diagram below. This study allows the researcher to discover general attitudes and perception that people have on personal, technological and transactional levels. To determine the connection and effects these attitudes have on e-commerce is paramount to developing e-commerce. The facets surrounding this study revolve on the following;
Security and privacy: the perception of e-commerce portals as secure platforms without any uncertainty and adverse consequences after e-commerce use, and the ability to determine when and what extent information about them is communicated to others for maintaining confidentiality.
Trust and Loyalty: the willingness of people to rely on and willingness to frequently use e-commerce portals for conducting transactions based on the feelings of confidence and assurance.
Accessibility and Awareness: the perception of user interface quality and the degree of awareness on information about products and services delivered from conducting transactions from any location at any time through e-commerce portals. factors influencing e-commerce
Quality and benefits: the perception of quality of products and services offered from e-commerce portals and benefits that arose from conducting such transactions.
Figure 1: The Research Model
5. Implications for Ecommerce in Developing Countries
In developing countries, IT and communication or rather e-commerce growth are substantial. Technology effectiveness is essential in E-Commerce success. However, human, economic, and other organizational issues must be taken into account as well. In this study, we evaluated the current status of E-Commerce in Developing countries. The evaluation of current status reveals opportunities that should be seriously tackled by organizations, if they are to survive the consequences of globalization and open markets. There should be an immediate implementation of a governmental infrastructure to support e-commerce. This thesis explored the areas enabling and huddles to the development of e-commerce. Online consumers face problems concerning security and privacy. They are exposed with online risk such as hacker mischiefs. Moreover, when buyers make payment using credit cards, they are exposing their banking information which could also be manipulated by hackers. The results of this research showed that majority of the respondents felt that internet shopping is risky due to the same reason. Amongst the perceived risks is financial, product performance, social, psychological and time convenience loss. Other than stolen credit card information, there are also risks in delivery. The time taken for delivery may take quite some time, therefore, anything could happen in the process of delivery. Buyers may lose the item. Online vendors might not be responsible for the loss and this leaves the buyers to bear all the consequence. When the perceived risk is greater, the relationship between intention and online purchasing will be weakened. factors influencing e-commerce
The implementation of an effective Internet e-commerce solution in Developing countries or other country that want to develop its e-commerce system can consider the following key steps: Developing strategy; before implementing Internet e-commerce, an organization must clearly define its goals. Many companies create goals that are not measurable or specific. Assessing readiness; before taking on the complexities (and risks) associated with implementing Internet e-commerce, an organization and its management should take stock of their current systems and capabilities. Four key drivers predict an enterprise’s ability to succeed in e-commerce. These four drivers are: leadership; governance; competencies; and technology.Designing the project; Although projects will differ greatly in the details, there are some common requirements for implementing Internet e-commerce, including: managing the project, developing an outsourcing strategy, selecting an Internet service provider, selecting e-commerce service providers; and designing website security. Integrating the solution; In developing an Internet e-commerce platform, an organization must also consider how to integrate its e-commerce applications with its other business processes. For example, the richness of corporate intranet applications positively affects e-commerce capabilities. Extending intranet applications into the Internet permits an organization to provide more value to customers in several ways: real-time access to information; and ability to perform business transactions. Measuring effectiveness: Given the major investment that implementing e-commerce entails, it is only common sense to measure the return. Successful e-commerce companies have serious and accountable metrics and clear agreements about using them across the organization. It is in the appropriateness and completeness of the metrics selected that typically set successful e-commerce implementations apart from the ones that are unsuccessful.
Under the guidance of grounded theory and through analyzing and synthesizing the gathered data, a content analysis of e-commerce enablers and disablers in developing countries was constructed.
This research highlights the most important factors that need to be considered in order to support the proliferation and advancement of e-commerce. Countries need to encourage and improve the e-commerce developments. This research sheds light on the potential factors that may play a significant role in supporting the proliferation and advancement of E-Commerce in developing countries. The outcomes of this study may contribute to the market stakeholders’ understanding of their potential customers’ needs and current concerns. Exploring the market, especially at this time while e-commerce is still in its development stage, is critical for industry stakeholders in order to ensure the success of this emerging market. Future research should focus on studying the development of e-commerce and testing the research model. Consequently, potentially important dimensions of the study could include an investigation in multiple cities, and especially in more rural areas, which may lead to more accurate and comprehensive results and analysis. Also, comparative research in different parts of the world would produce more complete findings. The results of this study could then be compared with those of other developing countries having similar conditions to see if there is a significant difference.
Key takeaway
- The availability and continued growth of Internet technologies (IT) have created great opportunities for users all over the globe to benefit from IT services and use them in a variety of different ways. The use of IT to conduct business online is known as Electronic Commerce (E-Commerce).
- We are witnessing a boom of new technologies, especially in the service sector (IT, Telecommunications, Internet, etc.). Due to technological advances economic transactions have become much easier and faster and this is mainly because of the development of e-commerce. Real engine of the new economy, e-commerce is a remarkable source of competitive advantage for businesses and a new space for consumers. In the coming years, growth and profitability will depend most likely the ability to introduce these new emerging technologies and adopt new methods of business transactions. Since many years ago computers, appliances, plane tickets and many other items are available for purchase on the Internet using cards issued by local banks. Although this technological trend could significantly strengthen the national economic structure, its role and place in developing countries economic structure remains unclear and leaves many questions to ask:
Most people have wondered how new online stores are able to offer the variety of inventory that is needed to compete with established brick and mortar outlets, and the e-commerce vendor is at the heart of that answer. E-commerce vendors are needed to supply the software and services used to start and operate most online stores. However, they are more prominently known for supplying consumable and durable goods to online shop owners so that they can resell the items at a profit. As many people realize their dreams of store ownership by opening their own electronic retail stores, there is an increase in the need for suppliers for this fast paced niche sector within the retail industry. E-commerce store owners must choose suppliers that are agile, flexible and quality oriented, or they risk being driven out of business by competing e-shops that have leaner, more reliable supply chains.
One of the most exciting ways that online stores can get up and running very quickly and with plenty of product offerings is by using drop shipping vendors, according to Practical eCommerce. These vendors allow retailers to take orders from customers over their websites, and the vendors deliver the products directly to the purchaser. It sounds very easy, but there are some drawbacks. For instance, the online retailer must rely on the drop shipper to make appropriate deliveries of undamaged products to their customers within specified time periods. Since the vendors have many different customers, there are bound to be mistakes. The online retailer must be ready to field customer complaints when this happens. Also, the profit margins on the drop shipped items are low because the e-commerce vendors are doing most of the logistical work and inventory storage. The wholesaler is another type e-commerce vendor. Online store owners can purchase items from wholesalers that are below list prices and resell them to their online customers for a profit. Even though higher shipping costs are involved, the profit margins that online retailers gain by using overseas wholesale suppliers are almost always larger than when they use domestic wholesalers. However, online retailers must watch for quality issues when using overseas supply companies that beat out the competition through the use of cheap labor. Online retail business owners who sell specialty goods often find that the best e-commerce vendors are the manufacturers of the goods. These e-shop owners can establish purchase agreements with manufacturers, and the results are lower prices and potentially higher profits from sales.
Characteristics of Reliable E-Commerce Vendors
Reliable e-commerce vendors have quality control systems in place to ensure that purchased products are delivered without damage. The best way for online retailers to find out about the quality control practices of potential e-commerce vendors is to go through a company that pre-screens vendors. The pre-screening service helps to reduce the chances of retailers falling prey to scam artists, and they often highlight their quality control practices and past performance. Reliable e-commerce vendors also work with retailers to solve unexpected problems instead of leaving the online retailer to handle customer care nightmares on their own. Retailers can get good indicators of the quality of the vendors’ services by checking if near competitors or leaders in the market are being supplied by them. If market leaders have been serviced by the vendor for a long period of time, then the vendor probably has a sustainable track record for success.
Maintaining Good Retailer Vendor Relationships
Success with e-commerce vendors takes work just like all business and personal relationships. Online retailers can establish trust with their vendors by maintaining good payment histories. They can continue building lasting business partnerships by deviating as little as possible from their vendors’ ordering systems as possible; if the vendors have many customers, they probably do not want to waste time processing orders that do not fit their predetermined formats. Making friends with vendors is a definite positive, as it becomes easier to educate them about one’s unique product requirements; for example, vendors might be willing to go the extra mile for a friend as opposed to someone who just places online orders from them.
Conclusion
Vendors for e-commerce retail sites have become key elements of the supply chain for many business owners. Depending on the type of products sourced and the number of customers that the vendor supplies, the process of providing the appropriate products at the right time can get complicated. Subsequently, online retailers realize that the same tried and true principles of supply chain management are applicable when doing business with an e-commerce vendor as they are when applied to a traditional supplier.
Key takeaway
- Most people have wondered how new online stores are able to offer the variety of inventory that is needed to compete with established brick and mortar outlets, and the e-commerce vendor is at the heart of that answer. E-commerce vendors are needed to supply the software and services used to start and operate most online stores.
- However, they are more prominently known for supplying consumable and durable goods to online shop owners so that they can resell the items at a profit. As many people realize their dreams of store ownership by opening their own electronic retail stores, there is an increase in the need for suppliers for this fast paced niche sector within the retail industry.
- E-commerce store owners must choose suppliers that are agile, flexible and quality oriented, or they risk being driven out of business by competing e-shops that have leaner, more reliable supply chains.
Planning, designing, and scheduling are the primary and crucial stages of any business practice; either it is an offline or online business. Outlining of the ecommerce website will help you to jump on to the originality regarding user experiences and product value in the market rather than imaginations.
Well, if you are willing to start ecommerce website then surely you need to hire ecommerce website developers. Make sure that hired fellows have enough technical knowledge regarding the different phases of ecommerce website development such as planning, research, designing and launching.
Below are some essential stages of ecommerce development which are certainly required for any successful ecommerce website:
The ecommerce website should be designed in a way that the candid interactions can be done between the professional ecommerce website Development Company and users. Hence, agendas of website development company should be well-understood by the website designers. To meet this need, the frequent conversation is necessary between website designers and company developers.
This will help to estimate the round figure of users and determine the breakthrough keywords by which the audience will explore your ecommerce website development company. This is the most efficient way to fascinate more right users rather than expending money on marketing strategies.
2. Preparation of Website Outline
This step is one of the crucial stages of e-commerce development. It includes considering the needs of ecommerce Website Company and the users and making efforts to meet them bit by bit.
Consider yourself as a user for a moment and try to cover all the requirements of your clients such as content, search and landing pages. This will also give the idea of crucial information which you should add up on your website to convince your users.
Moreover, this will give you the exact idea of how the customers approach your website and how much time they spend on your website. Moreover, it will also enable the information regarding visited pages of your website by the customers.
The information texture will reflect outlines of your ecommerce website. This will be the core portion of your website as people visit your website quickly if they will find what they are looking for. Hence, you should adopt some effective information practices to portray your product in well-organized and well-defined manner. All in all, as your website accessible and informative as the users, will visit and become your customers.
This stage is formed to appeal the customers using a graphic representation of your ecommerce website. This stage needs lots of creations and animations for the display of knowledge and detailed information regarding your ecommerce company and product.
Using different software, the prospector of your company will be designed. These templates contain the information regarding company’s agenda, strategy, principles, and products. It also covers the ecommerce website development services which company offers to the users. Moreover, your company’s fame and success will be represented in the form of videos or images.
This is the backbone of any ecommerce website. This process includes user, server-side applications such as CGI scripts, incorporation of third party tools and solutions, which will enable more accessibility of your ecommerce website.
Moreover, third party tools, server-side applications, and few essential elements collectively function well and make the number of users of the ecommerce website. You can simply compare the construction procedure with the building framework and web designing with the walls.
Hence, website construction is a crucial portion of the ecommerce website development. So adoption of effective web construction practices will be helpful to strengthen the other elements of website developing.
It is the last and essential step of the ecommerce website developing. This is the stage when you shift your website from the development server to the launching mode. It is also the time to re-check each and every content of your website.
Moreover, the reassessment of the information should be done, which is displayed on the website regarding your brand and product. However, the reassessment of website elements is necessary for all the stages of ecommerce website development.
Development of ecommerce website needs correct research about the product and ecommerce website owners. Moreover, adoption of effective practices such as the use of client-oriented applications, animations, display of owner’s success oriented images will be handy for enhancing the users and clients.
You should make sure that your website is easily accessible for the users. The frequent conversation between website owner or partners and the hired website developers is essential to design the ecommerce website as per the requirements of owners and users. After finishing the web design, launching of the website takes place. Hence, the journey of ecommerce website gets started.
Key takeaway
- Planning, designing, and scheduling are the primary and crucial stages of any business practice; either it is an offline or online business. Outlining of the ecommerce website will help you to jump on to the originality regarding user experiences and product value in the market rather than imaginations.
- Well, if you are willing to start ecommerce website then surely you need to hire ecommerce website developers. Make sure that hired fellows have enough technical knowledge regarding the different phases of ecommerce website development such as planning, research, designing and launching.
Business development is a somewhat-ambiguous term with a function and responsibility that varies from company to company.
While the definition has been endlessly debated, the ultimate goal of business development is to find strategic opportunities that create long-term value. This requires effort from brand marketing, sales, partnerships, and ultimately depends on the delivery of quality products to match these efforts. Essentially, BD applies to every area of a company.
Business development is often used interchangeably with sales, which underestimates the many other considerations necessary to execute on strategic business initiatives. While sales is an important component of BD, it's one of several key factors that go into creating value for a business.
The broad definition of business development underlies just how crucial it is to success in any industry, and ecommerce is no different.
Business development is built on relationships
Through its varied applications, every area of business development has one thing in common: it depends on building relationships - with customers, partners, and departments within a company. Every company relies on other organizations and all of its departments to get their product or service to a customer, and building strong business relationships is necessary to succeed in any field.
Consider a pro football team: its objective is to win games and increase profits. But to achieve that, the coach needs to be in sync with the players, general manager (chooses players and oversees budget), training staff (monitors player health), PR (manage distractions), and owner (verifies expenses), who all play an integral role in building a profitable championship team. With a unified front established, the team can then work efficiently with third party contractors and organizations to fulfill all outstanding needs.
Much like the above example, it's important for an ecommerce company to establish clear objectives that are translated into goals for each department. A target market must be established to select the right products for a determined audience, and brand messaging should reflect these principles. A healthy line of communication between departments ensures that individual objectives are aligned to meet company goals; from there, each team works to forge additional strategic partnerships to reach their targets.
What is business development for ecommerce?
Once goals are set and each department knows what it needs to do, an ecommerce business inherently relies on other organizations to complete every step necessary to get the product to customers. While every company has its own unique BD needs, common business relationships include:
- Shipping: Reliable and timely deliveries are necessary to keep customers happy, and this depends in great deal on the shipping provider. An online store must be responsible for a shipping provider's fulfillment regardless of fault, making this an extremely vital partnership. Factor in the cost and corresponding economic implications, and this is an alliance that can make or break an online store.
- Supply: Product fulfillment depends just as much on suppliers as it does on shipping. Being in sync with a supplier is crucial to maintaining inventory, keeping the promise to customers, and scaling your business.
- Marketing and advertising: Effective digital marketing is quite work-intensive, which is why many ecommerce businesses seek outside help for SEO, PPC, email marketing, and display advertising. Another important consideration is content marketing, which requires both quality curation and strategic distribution to be successful.
- Product: Offering products to complement your main offerings--accessories--helps fulfill customer needs and increase retention. When you can't get these from a primary supplier, it can be accomplished by direct partnerships with manufacturers.
- Customer service & PR: Perception is reality, especially in the online marketplace where one bad review can preemptively end your relationship with a customer. Established enterprises often partner with PR agencies to generate positive press and manage negative publicity. One of the best ways to ensure customers stay happy? Excellent customer service. This often requires an additional partnership, whether with live chat software, a help desk application, or a third-party call center.
Key takeaway
- Business development is a somewhat-ambiguous term with a function and responsibility that varies from company to company.
- While the definition has been endlessly debated, the ultimate goal of business development is to find strategic opportunities that create long-term value. This requires effort from brand marketing, sales, partnerships, and ultimately depends on the delivery of quality products to match these efforts. Essentially, BD applies to every area of a company.
- Business development is often used interchangeably with sales, which underestimates the many other considerations necessary to execute on strategic business initiatives. While sales is an important component of BD, it's one of several key factors that go into creating value for a business.
- The broad definition of business development underlies just how crucial it is to success in any industry, and ecommerce is no different.
A Business Case can be a powerful tool in obtaining the funds you need to drive change in achieving optimally performing systems. We explore 9 common components of a well written proposal.
Navigating the world of submissions and proposals can sometimes feel like a juggling act. With your day to day workload and an ever changing industry it may be difficult to secure capital for investments to return long term benefits.
Although procurement of funds for requirements such as preventative maintenance may be easier to obtain through OPEX, the focus has traditionally been on short term benefits. Whereas in the longer term, capital investment can provide performance and economic benefits that outweigh short term gains.
While maintenance is a necessary ongoing cost, advancements in technology such as fault detection, isolation and restoration offer the possibility of reliability improvements for larger and longer-term benefits to utilities and consumers.
Maximise the impact of your business case with these key elements:
An executive summary should provide the following:
- A brief snapshot of the problem that you are addressing
- An overview of possible solutions to achieve cost and performance benefits
- Include contributors and people that you have consulted to reflect internal support and provide the decision maker with further confidence in your Business Case
Be aware of your organisation’s overall strategy and goals. If your proposal is counter intuitive to these goals gaining approval for funds can become more difficult. Keeping in line with your organisation’s strategy shows a clear path to how your project can help the business achieve its targets.
It is important to have an understanding of whether or not your Business Case requires a philosophy shift in the way your organisation is structured and/or operated. Taking into account a broader view that looks at the ripple effect outside of the short term expense of your project can add more credibility and substance to your proposal, as well as assist in understanding where change is needed.
A concise and informative project outline based on reliable data can add weight to your Business Case. These fundamentals will help the reviewer gain a better understanding of your proposal:
- Clearly state why you are proposing the project, making sure business needs are addressed
- Include a clear analysis of the problem
- If reviewers fail to understand the problem they will not connect to why resolving it is necessary, which in turn can limit the success of your Business Case.
- Provide data that shows urgency of the problem
- Define what areas of the business are being affected
- Include options to resolve the problem and relate the remaining sections of the proposal to these options
- If you are including a status quo option, one that requires no change from the current situation, it is important to address the impact of doing so, especially in terms of how it will or will not address the problem being faced
- Include details of alternate timelines if the options have different schedules2
- Reference industry standards and guidelines that your project aligns with as this can have a positive effect on cost savings
- Utilise visual tools where necessary to ensure the project will be clearly understood
A detailed timeline and strategic plan should cover:
- How you will achieve the desired outcome including key milestones and significant deliverables2
- What resources will be required
- Clear indication of the required roles and responsibilities
- How the project will be monitored and what Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) will be implemented to ensure targets will be achieved at the various stages
- Whether your plan will have an impact on existing organisational events such as shutdowns, corporate, operational and/or structural changes. It is also worth noting if such events will have an effect on your project.
Benefits can be defined as detail savings in terms of revenue and productivity that are a result of achieving greater efficiency.2 An effective representation of benefits typically includes:
- Measurable financial benefits which will be used later for comparison against costs to reflect the actual Return on Investment (ROI)
- Societal impacts such as increased staff morale or consumer satisfaction can be included but should not be the primary focus
- Detailed information on the source of your data and assumptions regarding calculations adds further credibility to your proposal.
It is critical to cover all potential risks as decision makers will be looking for analysis that includes:
- Risks associated with the problem and the likelihood of these occurring in easy to define terms, i.e. low, medium, high
- Consideration of threats and opportunities that can inhibit or maximise return from the project
- Risks related to proceeding or not proceeding with the proposal
- Specific risks linked to the various options presented
For a comprehensive proposal it is imperative to ensure all costs are detailed clearly and concisely. Quantifiable costs relating to CAPEX can be categorised into one or more of the following:
- Reliability
- Security
- Efficiency
- Performance Improvement
- Safety
Non-quantifiable costs such as credibility and reputation should be acknowledged ideally in terms of how they impact quantifiable costs and benefits.
Present your final recommendation and why you have come to this conclusion. Highlight the benefits and costs involved, and ensure the recommended solution clearly shows the greatest ROI. Easy to understand formats such as tables are powerful tools in relaying your point to the reviewer. As most of the detail has already been covered, you can present this information in a summary format.
The concluding summary is your opportunity to emphasise the crucial parts of your Business Case that you want decision makers to remember. It should include:
- The problem and business need - why you are putting forward your Business Case
- Benefits and risks of the options - solutions to the problem
- Return on investment - what the overall gain will be to the business
- Final recommendation - based on the information presented
Key takeaway
- A Business Case can be a powerful tool in obtaining the funds you need to drive change in achieving optimally performing systems. We explore 9 common components of a well written proposal.
- Navigating the world of submissions and proposals can sometimes feel like a juggling act. With your day to day workload and an ever changing industry it may be difficult to secure capital for investments to return long term benefits.
- Although procurement of funds for requirements such as preventative maintenance may be easier to obtain through OPEX, the focus has traditionally been on short term benefits. Whereas in the longer term, capital investment can provide performance and economic benefits that outweigh short term gains.
The number of people shopping online is increasing day by day as it is convenient to do so from anywhere. If you have a physical store, you should consider building an online store too, as it is a great way to make extra money. Also, having e-commerce solutions for your business is a smart and cheap way to reach the global audience.
The development process of an online/e-commerce store is hard if you have no clue where to start. But the good news is that to build a good custom e-commerce site doesn’t require much money, time or technical knowledge.
With the right knowledge of e-commerce platforms like Shopify, Wix, and BigCommerce, you can quickly develop your online site. You can even hire an e-commerce website development company for creating your website. All these platforms are easy and cheap to use whether you use it to develop yourself or hire an ecommerce web development company.
There is no coding required, but you do need to a full guide about how to use these tools for developing your online store. It is exactly what we will do in this blog.
The 11 steps that will guide to develop an e-commerce website
1. Find the website builder that fits your needs
There are numerous ecommerce platforms available in the markets that are easy to use. Some of the tools are expensive while others are affordable. So, let’s list some of the best tools and their features for your online store development.
- Shopify
The best ecommerce development platform is Shopify. It has tons of features that will help you develop a scalable online store. It has the ability to sell products across many social platforms like Facebook, Amazon and so on.
- Wix
Wix is best suited for small businesses and startups. It has more than 510 templates that suit all genres of business like sports, beauty and so on. All the templates are optimized for mobile use. Other features include adding product videos, editor and easy user-interface.
- BigCommerce
Another great platform for your eCommerce site is BigCommerce. It creates a scalable site and has great SEO tools and has many more features than its competitors.
- Weebly
With plenty of features with drag and drop being one of them, it is the easiest platform. The best feature of Weebly is that it lets you create dedicated pages for all your products.
- Magento
The current favorite tool for developing online store is Magento. All over the globe, the developer prefers it. It integrates advertisement, analytics, and content creation and so on to provide the best user experience.
Some other eCommerce website development platforms are- WordPress, Big Cartel and so on.
Why to use these tools for building your online site?
A developer can make a website from scratch using coding and programming. It will take time, but the end result is great. So, why use these tools?
- These website building tools host your site on the internet.
- It aids you in buying a domain name.
- They are secure and have certificates to prove that. It helps to keep the payment getaway and customer details safe.
- It monitors your site continuously so that it runs smoothly.
Now, you must be confused about choosing the right platform. Don’t, check with your team and find out the purpose of your online store. Once you are clear on that, the right platform will be easier to find.
2. Test the tool
Before you start with the development process, test the tool to find out any discrepancies. For a successful online store, this step is crucial. To test the e-commerce development platform, all you have to do is sign-up for the free trial and start exploring.
Here some things to check in the test which will help you find the right tool:
- How easy is it to customize the features or modify it?
- Are the templates/theme provided suits your business? Also, check whether it’s easy to choose them or not.
- How is the navigation feature and can you customize it to add sub-menus and all?
You can make a trial site and check out all these and other things that you require for your business.
3. Buy the right plan for your business
Once you have finalized your e-commerce site development platforms and tested it. It’s time to choose a plan for starting the development process. All these tools come with many plans- free, paid version for individual and paid version for companies.
According to your need and size of the online store, you will have to choose the plan. A free plan of all these platforms supports minimum selling of products and runs up to 15 days.
If you want to build an e-commerce store, you need more features, and functionalities, which mean buying the full version. If you want a small online store, maybe you can develop it using the free version.
4. Register for a domain name
A domain name is the part of URL that has the name of your business. It is crucial to have a good domain name as it builds trust and brand with your consumer. With the help Shopify, Wix and BigCommerce platform, you can buy a great domain name in around $10-$20 per year.
Here are some tricks and tips to select a correct domain name for your eCommerce solution:
- Country code: Picking a correct country code is crucial. If you plan to sell your product to only international clients, use a dot com (.com) domain. If selling to a specific county, then you can use their code. Like Amazon has both .com for US and international consumers and .in for selling just in India.
- No brand name: Avoid using brand or product name in the URL as it can get you into legal troubles.
- Unique: The domain name should be unique, but not so weird that people find it hard to look on a search engine.
- Integrate a keyword: In the domain name, add a term that resonates with your business. The keyword will help you to have a higher rank in search engines which will ultimately get you more traffic and sales.
If you already have a domain name, you can link it with your online store or cancel that agreement.
5. Pick template for your website
Templates also known as themes make your site appealing. Most e-commerce platform lets you design and develop your own site too, but that requires coding. So, if you want to avoid that, use these templates.
Here are some tips for choosing the right template:
- Features you want in your store: Features are the key to a good website. So, brainstorm and decide which feature is more important for your store. It can be mapped, about us page and so on. Make a list of features and use it narrow down the template.
- Homepage style: Homepage is the first thing consumers will notice about your e-commerce site. So, make sure that the chosen template does justice to it. Based on your business goals, decide what you want more videos, sliders, single image and so on.
- Smooth navigation: The navigation of the website should be simple and helpful. A potential customer will surf through the site for 10-20 seconds if the template’s navigation feature is weak; it means that they won’t find what they are looking for easily. It will amplify bounce rate of the website.
Other than that, check out the font and color of the template. It should go with your brand image and should not be offensive.
6. Customizing the template
After choosing the template, the e-commerce development tools allow the user to customize it. For customization, you will have to go to the store’s admin panel. You can modify anything according to your will.
- Text Size, Color and Font
- Color of the theme
- Use of images
- Product’s position and so on.
7. Time to add the products
Once you have customized your template, it’s now time to add products to your website. There is a button that will guide in adding your products. You must add these details to your product to make it more alluring consumers:
- Name of the product and name of the brand (If outsourcing)
- Price of the good
- Category
- Weight for physical things
- File (For eBooks and all)
All the platforms have a different policy when it comes to a number of products, product description and variation you can add.
A product description is crucial to get the attention of the consumer along with images and category.
Check out these pro tips for the description:
- Don’t use a long sentence to describe the product. No one has that much time.
- Don’t use cliques or technical jargon while describing a product.
- The description should also be SEO optimized as it will help you rank higher and get more traffic and sales.
For product image:
- The images used should be high in quality and must not be blurry.
- The size of every image must be the same.
- The photos of the product should be taken with a piece of good quality equipment.
- The image should be visible from every angle, so a 360-degree option is necessary.
- The image should have a zoom button.
- The images used should be optimized so that they don’t slow down your website’s speed.
For product category:
- Price range so that people pick products that they can afford.
- Option to filter the product using price, size and so on.
8. Payment methods
Online stores will be incomplete without payment gateway. It is a crucial step in converting a consumer into a buyer. E-commerce development tool makes integrating payment methods of all kinds into the site easy.
They connect the user directly to PayPal, Apple and Google Pay, Credit/Debit cards, Master or Visa Cards for paying. The option to pay on delivery is also available.
Payment option:
There are three popular payment options:
- Merchant account and payment gateway: In this option, you partner up with a bank and they accept payment on your behalf. After this, they transfer the amount to your business account.
- Payment gateway packages: In this option, software integrates all the option into one and processes your card payments.
- Credit card payment: In this option, the payment method is integrated with the store’s cart which means you don’t have to leave the site to complete your payment.
Tips to apply the best payment method for your online store:
- To find out which payment methods work for your site, keep these things in mind:
- Figure out the estimated number of total sales
- Customer details are also crucial. Find out, where the customer is from so that you can have a payment getaway preferred by everyone.
- The payment method should also go with your store’s purpose and needs.
Security measures:
Customer worries most about security as they share their private details online. So, making the site secure should be your priority, and it’s also easy to do so.
The website building tools use SSL certificates to secure the website. Secure Socket Layer encrypts user data and optimizes user experience while online shopping secure.
SSL is inbuilt in the tool. If not, it will be available as an add-on.
What is the cost of these Payment Options?
- All the different payment methods have different charges. Since, it comes bundled with other features, de-tangle them. Figure out how much you are paying and for what? Keep the following points in mind:
- You cannot avoid the credit card fee. The provider sets the fee which is passed on by the platform.
- The charge on using payment processors varies from 1%+ 10p to 3% + 30p per transaction.
9. Shipping settings
The next step is to set up the shipping settings so that you can deliver the products on your website.
Different e-commerce platforms have different options, but to set up this tab, you will need these details.
Address of the shipping office:
- Include the address of the shipping origin to calculate taxes and all. It also makes printing labels and asking for quotes easy.
- Address of shipping origin office is required when products are not shipped from the main office.
- Shipping zones you want to cover:
- Shipping rates vary between countries and Zones. All development tools allow the user to charge different rates from consumers based on their zones.
- The admin page shows your shipping zones and the individual rate of shipping for each zone.
- Different shipping options are:
- Here is how you can ship products to different zones:
- Free shipping: If you sell a luxury product and can afford it, this is the best option. Also, set the option of free shipping after a certain value. If your online store sells products that are affordable, then don’t pick this option as it won’t be profitable for you.
- Flat rate: In this option, you use the same amount for shipping any product. It is a great marketing tactic, and you can cover the entire country or some district in one price range.
- Real-time price: The shipping charge depends on the product’s weight, size and so on. It is good for products that are expensive to ship for free.
- Pickup by a customer: A great option is to ask the consumer if they want to pick the parcel from a local store or the office.
Different shipping services:
- The online store building tools allow you to provide different shipping options to your consumers. It includes paying more for a one-day delivery and so on.
10. Settings for the store
Your online store needs to run properly every single minute and this needs proper settings. You can do this by filling out your preferences for each of the following in the store setting section of the tool.
- Language: Select the language that the customer will see on the website
- Currency: The currency you want to deal in
- Time zone: To track the orders, set up your time zone.
- Address: Contact information and address of the main and local office.
- Store Name: Name of the store that you want on the title, homepage and other pages and online searches.
- Contact Details: A public phone number and an email address
- Setting for the order: In this, you set the option of adding tax to your product or not
- Product settings: In the product settings, you can decide what details about the product you want.
You can take help from the tool’s support team to figure out all this.
11. Test the whole site and then publish it
The last step before publishing your site is to test it. You need to make sure that every section of the e-commerce site works perfectly. Any issue can dampen the user experience and sales of your site, so be careful.
Here are things that you should monitor while testing your site:
Checkout process
- Make sure that the checkout process works by making sure:
- All payment methods work against an order
- Shipping charges, price and category, and other details are visible.
- Discount and coupon codes are there or not.
- Whether the taxes on the product is visible or not.
- Refund policy on the product works or not.
- The best way to check all this is by ordering a product and refunding it.
Functionality:
- Make sure all the links and buttons like zoom in button works or not. If any of the functionality of the sites doesn’t work, it will make you lose customers.
- Content:
- Whatever content you use on your online store, should be free of errors and should be original.
- Mobile optimized:
- Make sure that your website works on all mobile devices as people prefer their Smartphone devices more.
- Different browser:
- Make sure that the website is easily accessible on all web browsers. Check the loading time and speed and fix any issue before launching.
Take some time to check these things before launching the site as there is no room for errors in this stiff competition.
Conclusion
The development process of an e-commerce site takes some time and research, but the end-result will be satisfying. With the help of this guide, you can easily use any of the e-commerce website development tools and start creating your online store. Always double check your work and make a detailed plan before executing it.
Key takeaway
- The number of people shopping online is increasing day by day as it is convenient to do so from anywhere. If you have a physical store, you should consider building an online store too, as it is a great way to make extra money. Also, having e-commerce solutions for your business is a smart and cheap way to reach the global audience.
- The development process of an online/e-commerce store is hard if you have no clue where to start. But the good news is that to build a good custom e-commerce site doesn’t require much money, time or technical knowledge.
References
- Computer Fundamentals by: Anita Goel, Pearson Education India ISBN: 9788131742136
- Connecting with Computer Science, by Greg Anderson, David Ferro, Robert Hilton, Course Technology, Cengage Learning,ISBN:9781439080351
- Fundamentals of Computer : For undergraduate courses in commerce and management, ITL Education Solutions Limited, Pearson Education, ISBN:9788131733349
- Introduction to Computer Science, 2/e, ITL Education Solutions Limited, Pearson Education, ISBN:9788131760307
- Frontiers of Electronic Commerce, Ravi Kalakota, Andrew B. Whinston, Pearson Education,ISBN:9788177583922
- Internet: The Complete Reference, Margaret Levine Young, Tata McGraw Hill Education Private Limited, ISBN: 9780070486997
- On the Way to the Web: The Secret History of the Internet and Its Founders, A. Banks,Apress Publication, ISBN: 9781430208693
- Computers and Commerce: A Study of Technology and Management at Eckert-MauchlyComputer Company, Engineering Research Associates, and Remingto, Arthur L. Norberg, MIT Press (MA),ISBN:9780262140904
- Essential of E-commerce technology By V.Rajaraman, Prentice Hall Inida Learning PriviteLimitated ISBN 9788120339378
- E-commerce Fundamental and Application By Henry Chan ,Wiley ISBN:-978126514694
- Information Technology ByDr.KishorJagtap, Tech-Max Publications, Pune
UNIT- 1
Introduction to E-commerce Tools
Ecommerce, additionally referred to as electronic commerce or web commerce, refers to the shopping for and mercantilism of products or services mistreatment the web, and also the transfer of cash and information to execute these transactions. Ecommerce is commonly wont to talk to the sale of physical product on-line, however it may also describe any reasonably business group action that's expedited through the web.
Whereas e-business refers to all or any aspects of operative a web business, ecommerce refers specifically to the group action of products and services.
The history of ecommerce begins with the primary ever on-line sale: on the August eleven, 1994 a person sold a CD by the band Sting to his friend through his web site NetMarket, Associate in Nursing yankee retail platform. this can be the primary example of a client getting a product from a business through the planet Wide Web—or “ecommerce” as we tend to unremarkably are aware of it nowadays.
Since then, ecommerce has evolved to form product easier to get and buy through on-line retailers and marketplaces. freelance freelancers, tiny businesses, and enormous companies have all benefited from ecommerce, that allows them to sell their merchandise and services at a scale that wasn't doable with ancient offline retail.
Types of Ecommerce Models
There are four main kinds of ecommerce models which will describe virtually each group action that takes place between shoppers and businesses.
1. Business to client (B2C):
When a business sells an honest or service to a private client (e.g. you purchase a combine of shoes from a web retailer).
2. Business to Business (B2B):
When a business sells an honest or service to a different business (e.g. A business sells software-as-a-service for alternative businesses to use)
3. client to client (C2C):
When a client sells an honest or service to a different client (e.g. You sell your previous article of furniture on eBay to a different consumer).
4. client to Business (C2B):
When a client sells their own product or services to a business or organization (e.g. Associate in Nursing influencer offers exposure to their on-line audience in exchange for a fee, or a creative person licenses their icon for a business to use).
Examples of Ecommerce
Ecommerce will defy a range of forms involving completely different transactional relationships between businesses and shoppers, likewise as completely different objects being changed as a part of these transactions.
1. Retail:
The sale of a product by a business on to a client with none mediator.
2. Wholesale:
The sale of product in bulk, typically to a distributer that then sells them on to shoppers.
3. Drop shipping:
The sale of a product, that is factory-made and shipped to the buyer by a 3rd party.
4. Crowd funding:
The collection of cash from shoppers ahead of a product being offered so as to lift the start-up capital necessary to bring it to promote.
5. Subscription:
The automatic revenant purchase of a product or service on an everyday basis till the subscriber chooses to cancel.
6. Physical products:
Any tangible sensible that needs inventory to be replenished and orders to be physically shipped to customers as sales are created.
7. Digital products:
Downloadable digital merchandise, templates, and courses, or media that has to be purchased for consumption or authorised to be used.
8. Services:
A ability or set of skills provided in exchange for compensation. The service provider’s time may be purchased for a fee.
Key takeaway
- Ecommerce, also known as electronic commerce or internet commerce, refers to the buying and selling of goods or services using the internet, and the transfer of money and data to execute these transactions. Ecommerce is often used to refer to the sale of physical products online, but it can also describe any kind of commercial transaction that is facilitated through the internet.
- Whereas e-business refers to all aspects of operating an online business, ecommerce refers specifically to the transaction of goods and services.
The Internet was launched in 1969 when the United States funded a project that developed a national computer network called Advanced Research Project
Agency Network (ARPANET). The Internet is a large network that connects together smaller networks all over the globe.
The Web was introduced in 1991 at the Center for European Nuclear Research (CERN) in Switzerland.
Prior to the Web, the Internet was all text—no graphics, animations, sound, or video. The Web made it possible to include these elements. It provided a multimedia interface to resources available on the Internet.
It is easy to get the Internet and the Web confused, but they are not the same thing. The Internet is the actual network. It is made up of wires, cables, satellites, and rules for exchanging information between computers connected to the network. Being connected to this network is often described as being online. The most common uses are the following:
Communicating is by far the most popular Internet activity. You can exchange e-mail with your family and friends almost anywhere in the world. You can join and listen to discussions and debates on a wide variety of special-interest topics.
Shopping is one of the fastest-growing Internet applications. You can window shop, look for the latest fashions, search for bargains, and make purchases.
Searching for information has never been more convenient. You can access some of the world’s largest libraries directly from your home computer.
You can find the latest local, national, and international news.
Education or e-learning is another rapidly emerging Web application. You can take classes on almost any subject. There are courses just for fun and there are courses for high school, college, and graduate school credit. Some cost nothing to take and others cost a lot.
Entertainment options are nearly endless. You can find music, movies, magazines, and computer games. You will find live concerts, movie previews, book clubs, and interactive live games.
Access
When provided with a connection to the Internet, you can use a browser program to search the Web.
Providers
The most common way to access the Internet is through an Internet service provider (ISP). The providers are already
connected to the Internet and provide a path or connection for individuals to access the Internet.
The most widely used commercial Internet service providers are national and wireless providers.
National service providers like Comcast, Qwest, and Verizon are the most widely used. They provide access through standard telephone or cable connections. Users can access the Internet from almost anywhere within the country for a standard fee without incurring long-distance telephone charges.
Wireless service providers offer Internet connections for computers with wireless modems and a wide array of wireless devices.
Browsers
Browsers are programs that provide access to Web resources. This software connects you to remote computers, opens and transfers files, displays text and images, and provides in one tool an uncomplicated interface to the Internet and Web documents.
Browsers allow you to explore, or to surf, the Web by easily moving from one Web site to another. Four well-known browsers are Mozilla Firefox, Apple Safari, Microsoft Internet Explorer, and Google Chrome.
For browsers to connect to resources, the location
or address of the resources must be specified. These addresses are called uniform resource locators (URLs). All URLs have at least two basic parts.
The first part presents the protocol used to connect to the
resource. Protocols are rules for exchanging data between computers. The protocol http is used for Web traffic and is
the most widely used Internet protocol. The second part presents the domain name. It indicates the specific address where the resource is located. The last part of the domain name following the dot (.) is the top-level domain (TLD). It identifies the type of organization.
Once the browser has connected to the Web site, a document file is sent back to your computer. This document typically
contains Hypertext Mark-up Language (HTML). The browser interprets the HTML formatting instructions and displays the document as a Web page.
Today it is common to access the Internet from a variety of mobile devices like cell phones. Special browsers called mobile browsers are designed to run on these portable devices.
Communication
Some popular types of Internet communication are e-mail, instant messaging, social networking, blogs, and wikis.
E-mail
E-mailer electronic mail is the transmission of electronic messages over the Internet. All you need to send and receive e-mail is an e-mail account, access to the Internet, and an e-mail program. Two of the most widely used e-mail programs are Microsoft’s Outlook Express and Mozilla Thunderbird.
A typical e-mail message has three basic elements: header, message, and signature. The header appears first and typically includes the following information:
Addresses: Addresses of the persons sending, receiving, and, optionally, anyone else who is to receive copies. E-mail addresses have two basic parts. The first part is the user’s name and the second part is the domain name, which includes the top-level domain.
Subject: A one-line description, used to present the topic of the message. Subject lines typically are displayed when a person checks his or her mailbox.
Attachments: Many e-mail programs allow you to attach files such as documents and image files. If a message has an attachment, the file name typically appears on the attachment line.
Unwelcome mail is called spam. While spam is indeed a distraction and nuisance, it also can be dangerous. For example,
computer viruses or destructive programs are often attached to unsolicited e-mail.
In an attempt to control spam, anti-spam laws have been added to our legal system. For example, CAN-SPAM requires that every marketing-related e-mail provide an opt-out option. When the option is selected, the recipient’s e-mail address is to be removed from future mailing lists. Failure to do so results in heavy fines. This approach, however, has had minimal impact since over 50 percent of all spam originates from servers outside the United States. A
more effective approach has been the development and use of spam blockers, also known as spam filters. These programs use a variety of different approaches to identify and eliminate spam.
InstantMessaging
Instant messaging (IM) allows two or more people to contact each other via direct, live communication. To use instant messaging, you register with an instant messaging server and
then specify a list of friends.
The most widely used instant messaging services are AOL’s
Instant Messenger, Microsoft’s MSN Messenger, and Yahoo Messenger. One limitation, however, is that many instant messaging services do not support communication with other services. For example, at the time of this writing, a user registered with AOL cannot use AOL’s Instant Messenger software to communicate with a user registered with Yahoo Messenger. Recently, however, some software companies have started providing universal instant messenger programs that overcome
this limitation. Three widely used programs are Digsby, Pidgin, and Qnext.
SocialNetworking
Reuniting sites are designed to connect people who have known one another but have lost touch; for example, an old high school friend that you have not seen for several years. You join a social network by connecting to a reuniting site and providing profile information such as your age, gender, name of high school, and so forth. This information is added to the reuniting site’s member database. Members are able to search the database to locate individuals. Two of the best-know reuniting sites are Classmates Online and Facebook.
Friend-of-a-friend sites are designed to bring together two people who do not know one another but share a common friend. The theory is that, if you share a common friend, then it is likely that you would become friends. For example, a network could be started by one of your acquaintances by providing profile information on him- or herself and a list of friends. You could visit your acquaintance’s site to connect to a friend(s) of your acquaintance. You could even join the list of friends provided at the
site. Two well-known friend-of-a-friend sites are Friendster and MySpace.
Common interest sites bring together individuals that share common interests or hobbies. You select a networking site based on a particular interest. For example, if you wanted to share images, you might join Flickr or YouTube. If you are looking for business contacts, you might join Linkedln. If you wanted to locate or create a special interest group, you might join Meetup.
Blogs,Microblogs,andWikis
In addition to social networking sites, there are other types of sites
that help ordinary people communicate across the Web.
Many individuals create personal Web sites, called Web logs or
blogs, to keep in touch with friends and family. Blog postings
are timestamped and arranged with the newest item first. Often, readers of these sites are allowed to comment. Some blogs are like online diaries with personal information; others focus on information about a hobby or theme, such as knitting, electronic devices, or good books. Although most are written by individual bloggers, there are also group blogs with multiple contributors. Some businesses and newspapers also have started blogging
as a quick publishing method. Several sites provide tools to create blogs. Two of the most widely used are Blogger and WordPress.
A microblog publishes short sentences that only take a few seconds to write, rather than long stories or posts like a traditional blog. Microblogs are designed to keep friends and other contacts up-to-date on your interests and activities. The most popular microblogging site, Twitter, enables you to add new content from your browser, instant messaging application, or even a mobile phone. To learn more about Twitter, see Making IT Work for You: Twitter on pages 40 and 41.
A wiki is a Web site specially designed to allow visitors to fill in missing information or correct inaccuracies. “Wiki” comes from the Hawaiian word for fast, which describes the simplicity of editing and publishing through wiki software. Wikis support collaborative writing in which there isn’t a single expert author, but rather a community of interested people that builds knowledge over time. Perhaps the most famous example is Wikipedia, an online encyclopedia, written and edited by anyone who wants to contribute, that has millions of entries in over 20 languages.
SearchTools
A number of organizations called search services operate Web sites that can help you locate the information you need. Special programs called spiders continually look for new information and update the search services’ databases. Additionally, search services provide special programs called search engines that you can use to locate specific information on the Web.
SearchEngines
Search engines are specialized programs that assist you in locating information on the Web and the Internet. There are search approaches:
Keyword search: In a keyword search, you enter a keyword or phrase reflecting the information you want. The search engine compares your entry against its database and returns a list of hits, or sites that contain the keywords. Each hit includes a hyperlink to the referenced Web page (or other resource) along with a brief discussion of the information contained at that location. Many searches result in a large number of hits. For example, if you were to enter the keyword travel, you would get thousands of hits. Search engines order the hits according to those sites that most likely contain the information requested and present the list to you in that order, usually in groups of 10.
Directory search: Most search engines also provide a directory or list of categories or topics such as Autos, Finance, and Games. In a directory search, you select a category or topic that fits the information that you want. Another list of subtopics related to the topic you selected appears. You select the subtopic that best relates to your topic and another subtopic list appears. You continue to narrow your search in this manner until a list of Web sites appears. This list corresponds to the hit list previously discussed.
MetasearchEngines
Metasearch engines are programs that automatically submit your
search request to several search engines simultaneously. The metasearch engine receives the results, eliminates duplicates, orders the hits, and then provides the edited list to you.
SpecializedSearchEngines
Specialized search engines focus on subject-specific Web sites. Specialized sites can potentially save you time by narrowing
your search.
ElectronicCommerce
Electronic commerce, also known as e-commerce, is the buying and selling of goods over the Internet. There are three basic types of electronic commerce:
Business-to-consumer (B2C) involves the sale of a product or service to the general public or end users. Oftentimes this arrangement eliminates the wholesaler by allowing manufacturers to sell directly to customers. Other times, existing retail stores use B2C e-commerce to create a presence on the Web as another way to reach customers. The three most widely used B2C applications are for online banking, financial trading, and shopping.
Online banking is becoming a standard feature of banking institutions. Customers are able to go online with a standard browser to perform many banking operations. These online operations include accessing account information, balancing check books, transferring funds, paying bills, and applying for loans.
Online stock trading allows investors to research, buy, and sell stocks and bonds over the Internet. While e-trading is more convenient than using a traditional full-service broker, the greatest advantage is cost.
Online shopping includes the buying and selling of a wide range of consumer goods over the Internet. There are thousands of e-commerce applications in this area.
Consumer-to-consumer (C2C) involves individuals selling to individuals. This often takes the form of an electronic version of the classified ads or an auction.
Web auctions are similar to traditional auctions except that buyers and sellers seldom, if ever, meet face-to-face.
Business-to-business (B2B) involves the sale of a product or service from one business to another. This is typically a manufacturer–supplier relationship.
Plug-ins
Plug-insare automatically loaded and operate as part of a browser. Many Web sites require specific plug-ins to fully experience their content. Some plug-ins are included in many of today’s browsers; others must be installed.
Filters- Filters are used by parents and organizations to block certain sites and to monitor use of the Internet and the Web.
- File Transfer Utilities
File transfer utilities copy files to ( downloading ) and from (uploading) your computer. Three types are - File transfer protocol (FTP) and secure file transfer protocol (SFTP) allow you to efficiently copy files across the Internet.
- Web-based file transfer services make use of a Web browser to upload and download files.
BitTorrent distributes file transfers across many different computers.
Internet Security Suite - An Internet security suite is a collection of utility programs designed to protect your privacy and security on the Internet.
Key takeaway
- Electronic commerce, also known as e-commerce, is the buying and selling of goods over the Internet. There are three basic types of electronic commerce:
Business-to-consumer (B2C) involves the sale of a product or service to the general public or end users. Oftentimes this arrangement eliminates the wholesaler by allowing manufacturers to sell directly to customers. Other times, existing retail stores use B2C e-commerce to create a presence on the Web as another way to reach customers. The three most widely used B2C applications are for online banking, financial trading, and shopping.
There is rarely a facet within an industry that hasn’t been touched by technology. Most notably, big data and machine learning are paving the way for robotics automation, the instant transfer of data, and a variety of interesting devices.
The retail industry is no exception when it comes to taking advantage of technology. In fact, successful businesses are setting the bar by implementing technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), chatbots, and voice assistants into their operations. The reasons vary, but can include that these technologies help provide excellent customer experiences through instant communication, providing support without the help of live employees, data management and security, and much more.
Many online stores already have integrated e-commerce software, but to stay in the competition, any e-commerce business must give serious thought into the following technologies to stay prosperous and maintain customer satisfaction.
AI is revealing valuable insights into customer preferences — which can guide marketing campaigns. It also can provide for the automation and transfer of data management operations to increase performance. In the retail and e-commerce world, AI is being relied upon for several unique aspects of business.
74% of businesses believe that user experience is important for improving sales and conversions. AI provides a personalized user experience that 59% of customers say influences their shopping decisions. Artificial intelligence can facilitate a shopping experience that is supported by customers’ personal preferences.
AI, big data, and machine learning can offer analytics and foresight into customer behavior patterns which can drive advertising campaigns, provide support and services, and automate communication — all of which increase engagement rates for businesses.
Since AI can predict customer behavior patterns, it is able to recommend relevant and useful information to customers on products and services and more. AI and machine learning algorithms can efficiently forecast this information by taking in a customer’s search history and other third-party data. This can lead to effectively proposing applicable information and solutions to satisfy customer needs.
Customer behavior patterns are a driving force behind any marketing campaign. Using AI, businesses are able to target both potential and existing customers by looking at data such as past certain history. These analytics can be used to provide a better aimed content marketing strategy for businesses.
Content and advertisements may then be created with a tone that engages various audiences and placed on the correct media platform to capture their attention. Using AI and marketing automation can show a business the data necessary for a strategic and tactical campaign.
You will be hard-pressed to find a successful business that does not have at least one aspect of their business operations posted on the cloud. Managing and processing data in the cloud is essential for the instant access of data by anyone who needs it, on any device. Especially for e-commerce businesses, a cloud ERP can improve delivery speeds, make your store more adaptable, and bring about business stability and growth.
Recognized for their customer satisfaction rates and wide-scale availability, chatbots have pivoted from limited use in call centers to wide-spread e-commerce website applications. Rather than asking questions and providing information to those over the phone, e-commerce websites that utilize chatbots can provide a variety of services and solutions.
Many businesses cannot provide answers exactly when a potential customer is searching for them. Additionally, customers may be frustrated when put on hold because a business does not have the staff to answer and tend to a high volume of customers.
Chatbots are available 24/7, day and night, to provide any answers and solutions a potential customer may inquire about. Having this automated communication can be valuable for businesses as it frees up employees to focus on other business operations, efficiently communicates with customers, and may even propose products and services.
Built into a chatbot’s algorithm is what is called a decision tree. Decision trees use machine and deep learning to automate complex business processes, essentially developing, maintaining, and always expanding upon a comprehensive network of if/then statements.
By addressing commonly asked questions and concerns from customers, chatbots are able to expand upon their decision tree. Here, a chatbot can gain information on whether they’ve helped a customer or not. If they have helped the customer, this information may be passed on to another consumer with a similar question. If they have not adequately satisfied the customer, the chatbot may continue asking questions until they provide the customer with the information they are looking for. When they have answered the customer, the chatbot now has more choices in their decision tree to help customers in the future.
Send shipping and tracking information
Imagine if Amazon never remembered your address or payment information and never told you when your order is scheduled to arrive. It is a pain for customers to have to enter shipping information every time they want to order something from your e-commerce website. Additionally, it is a best practice for user experience to give a customer a timeframe for when the order will be at their doorstep.
Chatbots remember this information and can provide real-time shipping tracking details for customers. This can also help warehouse operations, as they could focus on the supply chain and fulfilling orders through their order management system rather than telling customers where their packages are.
Not everyone searches for products and information via mouse and keyboard in the digital age. To accommodate these potential customers, businesses will need to adopt voice commerce — using voice recognition technology and allowing customers to use voice commands to find and purchase products online. Voice assistants such as Siri, the Amazon Echo, and Google Home are becoming increasingly popular for their convenience in searching for and purchasing products. In order to stay successful, e-commerce businesses will need to provide this technology and its benefits to capture a new wave of consumers.
Any company jingle, music composition, or auditory tone is considered an audio brand signature. It is a way for businesses to better establish a brand identity, and help customers remember their name.
Businesses can command their audio brand signature to play through voice assistants to let their customers know where they are ordering their products from. By associating your brand with an auditory signature, consumers will know and remember they are ordering from your store – even when laying on their couch, speaking to a voice assistant.
Customers would rather automate their continual shopping needs than frequent a website (or store) every month for their essentials. Through voice assistants, people are able to compile shopping lists — ordering what they need from who they want. This technology learns the preferences of the owners, and many businesses are able to capitalize on brand loyalty. If a voice assistant knows that a person wants a product from your store monthly, it can add it to their shopping list. This can be beneficial to companies in forecasting sales and balancing order management.
In the marketing world, assistive technology and voice commerce are helping to reach a wide variety of new audiences — not just the younger generation who are using new devices, but the visually impaired as well. By using speech-to-text technology, the visually impaired can forgo the struggles of traditional search experience, and order what they need through new and developing assistive technology.
All interconnected, AI, chatbots, and voice assistants are becoming necessary for any e-commerce business to be successful. In order to stay with the times, businesses must adapt to these new technologies which appeal better to potential and existing customers.
Discover more B2B e-commerce trends and stats
- Get to know your customers: download our B2B Buying Process 2019 Report for stats and insights into the behavior, preferences and challenges of buyers, based on a survey of 500+ B2B customers.
- Discover the e-commerce trend toward B2B2C and D2C sales, including what other businesses are doing, and how you can respond.
- See how e-commerce trends have evolved and how to get ready for the future of e-commerce with our B2B e-commerce trends timeline.
- Understand the business benefits of ERP-integrated e-commerce based on a survey of global B2B and B2C customers.
Key takeaway
- There is rarely a facet within an industry that hasn’t been touched by technology. Most notably, big data and machine learning are paving the way for robotics automation, the instant transfer of data, and a variety of interesting devices.
- The retail industry is no exception when it comes to taking advantage of technology. In fact, successful businesses are setting the bar by implementing technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), chatbots, and voice assistants into their operations.
- The reasons vary, but can include that these technologies help provide excellent customer experiences through instant communication, providing support without the help of live employees, data management and security, and much more.
- Online shopping for retail sales direct to consumers via Web sites and mobile apps, and conversational commerce via live chat, chatbots, and voice assistants
- Providing or participating in online marketplaces, which process third-party business-to-consumer or consumer-to-consumer sales
- Business-to-business buying and selling;
- Gathering and using demographic data through web contacts and social media
- Business-to-business (B2B) electronic data interchange
- Marketing to prospective and established customers by e-mail or fax (for example, with newsletters)
- Engaging in pretail for launching new products and services
- Online financial exchanges for currency exchanges or trading purposes.
Key takeaway
- Online shopping for retail sales direct to consumers via Web sites and mobile apps, and conversational commerce via live chat, chatbots, and voice assistants
- Providing or participating in online marketplaces, which process third-party business-to-consumer or consumer-to-consumer sales
- Business-to-business buying and selling;
- Gathering and using demographic data through web contacts and social media
Four Traditional Types of Ecommerce Business Models
If you’re starting an ecommerce business, odds are you’ll fall into at least one of these four general categories.
Each has its benefits and challenges, and many companies operate in several of these categories simultaneously.
Knowing what bucket your big idea fits in will help you think creatively about what your opportunities and threats might be.
1. B2C – Business to consumer.
B2C businesses sell to their end-user. The B2C model is the most common business model, so there are many unique approaches under this umbrella.
Anything you buy in an online store as a consumer — think wardrobe, household supplies, entertainment — is done as part of a B2C transaction.
The decision-making process for a B2C purchase is much shorter than a business-to- business (B2B) purchase, especially for items that have a lower value.
Think about it: it’s much easier for you to decide on a new pair of tennis shoes than for your company to vet and purchase a new email service provider or food caterer.
Because of this shorter sales cycle, B2C businesses typically spend less marketing dollars to make a sale, but also have a lower average order value and less recurring orders than their B2B counterparts.
And B2C doesn’t only include products, but services as well.
B2C innovators have leveraged technology like mobile apps, native advertising and remarketing to market directly to their customers and make their lives easier in the process.
For example, using an app like Lawn Guru allows consumers to easily connect with local lawn mowing services, garden and patio specialists, or snow removal experts.
Additionally, home service businesses can use Housecall Pro’s plumbing software app to track employee routes, text customers, and process credit card payments on the go, benefitting both the consumer and business alike.
2. B2B – Business to business.
In a B2B business model, a business sells its product or service to another business. Sometimes the buyer is the end user, but often the buyer resells to the consumer.
B2B transactions generally have a longer sales cycle, but higher order value and more recurring purchases.
Recent B2B innovators have made a place for themselves by replacing catalogs and order sheets with ecommerce storefronts and improved targeting in niche markets.
In 2020, close to half of B2B buyers are millennials — nearly double the amount from 2012. As younger generations enter the age of making business transactions, B2B selling in the online space is becoming more important.
3. C2B – Consumer to business.
C2B businesses allow individuals to sell goods and services to companies.
In this ecommerce model, a site might allow customers to post the work they want to be completed and have businesses bid for the opportunity. Affiliate marketing services would also be considered C2B.
Elance (now Upwork) was an early innovator in this model by helping businesses hire freelancers.
The C2B ecommerce model’s competitive edge is in pricing for goods and services.
This approach gives consumers the power to name their price or have businesses directly compete to meet their needs.
Recent innovators have creatively used this model to connect companies to social media influencers to market their products.
4. C2C – Consumer to consumer.
A C2C business — also called an online marketplace — connects consumers to exchange goods and services and typically make their money by charging transaction or listing fees.
Online businesses like Craigslist and eBay pioneered this model in the early days of the internet.
C2C businesses benefit from self-propelled growth by motivated buyers and sellers, but face a key challenge in quality control and technology maintenance.
Five Value Delivery Methods for Ecommerce Innovation
If your business model is the car, then your value delivery method is the engine.
This is the fun part — where you find your edge. How will you compete and create an ecommerce business worth sharing?
Here are a few of the popular approaches taken by industry-leaders and market disruptors.
By cutting out the middleman, a new generation of consumer brands have built loyal followings with rapid growth.
Online retailers like Warby Parker and Casper set the standard for vertical disruption, but brands like Glossier are showing us how D2C can continue to be an area for innovation and growth.
2. White label and private label.
To “white label” is to apply your name and brand to a generic product purchased from a distributor.
In private labeling, a retailer hires a manufacturer to create a unique product for them to sell exclusively. With private labeling and white labeling, you can stay lean on your investments in design and production and look for an edge in technology and marketing.
In a wholesaling approach, a retailer offers its product in bulk at a discount.
Wholesaling is traditionally a B2B practice, but many retailers have offered it to budget-conscious consumers in a B2C context.
One of the fastest growing methods of ecommerce is dropshipping.
Typically, dropshippers market and sell items fulfilled by a third party supplier, like AliExpress or Printful. Dropshippers act as a middle man by connecting buyers to manufacturers. Easy-to-use tools allow BigCommerce users to integrate inventory from suppliers around the world for their storefronts.
As early as the 1600s, publishing companies in England used a subscription model to deliver books monthly to their loyal customers. With ecommerce, businesses are going beyond periodicals and fruit of the month clubs. Today, virtually every industry has seen the arrival of subscription services to bring convenience and savings to customers.
5 Examples of Innovative Ecommerce Business Plans
Many companies have flourished with the freedom ecommerce gives them. These brands have combined classic business models with something new, making them innovative leaders in the field.
In 2018, LARQ launched the first self-cleaning water bottle. This reusable, rechargeable bottle uses UV-C technology to eliminate viruses and bacteria in water, whether it’s from a tap or a natural source.
LARQ’s launch was the largest crowdfunded effort for a clean water initiative with $1.7 million raised. Today, LARQ donates 1%of its proceeds to efforts for clean drinking water around the world.
Buyers were attracted to this reusable bottle because of its eco-friendly factors, while they can also save money skipping on single-use water bottles, but still enjoy a clean water vessel (without scrubbing it) every time. These unique factors have led to LARQ’s increased revenue by 400% year-over-year.
2. Beer Cartel – Subscription service.
Some ideas sell themselves.
Beer Cartel offers Australia’s longest running beer subscription service, with expert-selected craft beers from around the globe delivered to subscribers’ doorsteps each month.
They’ve attracted the curious and the connoisseurs by giving their customers a unique selection at a price better than what they could get in stores.
Beer Cartel has also done a great job of offering several different subscription options to serve customers of all appetites and budgets.
Fortune 500 companies an family-owned startups alike trust Berlin Packaging for sourcing, designing, and distributing their containers and closures. As a hybrid supplier, Berlin Packaging brings their expertise to every level of the supply chain to increase efficiency and lower cost for their customers.
Berlin Packaging is over 80 years old but has kept their advantage by innovating every step of the way. By adopting an ecommerce business model, they stayed competitive by making it easy for their customers to shop from their large selection of containers sourced from more than 200 different partner vendors. Berlin Packaging also prioritized a strong connection between their site and ERP, making it easier for customers to see their credit limits, balances, and past due balances.
Atlanta Light Bulbs is no stranger to innovative ecommerce. ALB launched their first ecommerce site in 1999, which gave them a huge head start on creating a unique site experience for their customers.
As their market has shifted to the millennial generation, Atlanta Light Bulbs has focused on adding more to their online platform that will set them apart from their competition, such as using apps for their BigCommerce storefront.
Their mobile shopping app has primarily helped grow Atlanta Light Bulbs’ B2C sales, but even their commercial clients have come to enjoy the convenience of ordering from their mobile devices.
Another creative tactic from ALB is their make an offer feature, which allows buyers to name a quantity and price and submit an offer. On the backend, pricing rules are used to auto-calculate the lowest price Atlanta Light Bulbs can give. Customers receive a message letting them know their proposal has been accepted and they can checkout, or, if the price is too low, a different deal is offered.
5. Mountain Crest Gardens – Wholesaling.
Mountain Crest Gardens began as a family-owned and operated business in Northern California in the mid-90s. But when they relaunched their website in 2012, they saw 10x the revenue and a 400% increase in orders.
Mountain Crest Gardens capitalized on what made them unique: their aesthetically beautiful succulents. User-generated content organically amplifies the plants and drives orders. Plus, Mountain Crest Gardens caters to different consumers as they offer individual succulents, wholesale options and even a subscription box.
Selecting Your Ecommerce Business Model
We’ve talked about your broader options for choosing an ecommerce business model, now let’s look at the specifics.
Here are a few questions that will help you create a plan that will set your company apart.
The key here is honesty and research.
Spend time learning about the market you’re targeting and be honest about what unique value you can bring to the space.
Who are you looking to serve?
Consider what their expectations are when purchasing the type of product you plan to sell.
You’re most likely to succeed if you can understand their behaviors and habits and find ways to improve them or save money.
To do this, you’ll need to look for pain points in the way things are currently done.
This is where you as an innovator can carve a space for yourself.
What do you know better than anyone else?
Build around your existing strengths and the pieces that are energizing to you.
Be realistic about what elements you can do yourself and what you will need to find help for.
It can be challenging to know your limitations but it will help you make better long-term decisions.
3. What is best for your product?
Depending on your product, different models will serve you better than others.
For example, if you are manufacturing your own products, you may want to consider wholesaling or subscriptions to help cover production costs and break even more quickly.
If you are a distributor of other people’s products, you’ll want to invest more heavily into direct marketing and strategies that will grow your customer base.
You understand what makes your product better, but will consumers?
Evaluate your competition and make sure it’s clear why your product is the best choice.
Are you competing on price? Selection?Convenience?
From your back end processes, to your warehousing, to your marketing, to your website’s shopping experience, your unique value should be clear.
We’ve covered the most common ecommerce business models, several tactics for ecommerce innovation, and examples of ecommerce businesses that have blazed their own path.
We’ve talked about the questions you’ll need to answer to find a niche where your new endeavor can thrive.
Planning is important, but innovation doesn’t happen in a vacuum. It’s time to get your solution out into the world and begin to refine your business based on the feedback you receive.
Key takeaway
- If you’re starting an ecommerce business, odds are you’ll fall into at least one of these four general categories.
- Each has its benefits and challenges, and many companies operate in several of these categories simultaneously.
- Knowing what bucket your big idea fits in will help you think creatively about what your opportunities and threats might be.
The availability and continued growth of Internet technologies (IT) have created great opportunities for users all over the globe to benefit from IT services and use them in a variety of different ways. The use of IT to conduct business online is known as Electronic Commerce (E-Commerce).
We are witnessing a boom of new technologies, especially in the service sector (IT, Telecommunications, Internet, etc.). Due to technological advances economic transactions have become much easier and faster and this is mainly because of the development of e-commerce. Real engine of the new economy, e-commerce is a remarkable source of competitive advantage for businesses and a new space for consumers. In the coming years, growth and profitability will depend most likely the ability to introduce these new emerging technologies and adopt new methods of business transactions. Since many years ago computers, appliances, plane tickets and many other items are available for purchase on the Internet using cards issued by local banks. Although this technological trend could significantly strengthen the national economic structure, its role and place in developing countries economic structure remains unclear and leaves many questions to ask:
Where is the e-commerce today?
What are the obstacles to e-commerce? Is e-commerce having a bright future to become a mainstream business for growth, and what steps to take to get there?
While developed countries have harnessed and adopted E-Commerce, developing countries are not yet fully adapted to its adoption. The aim of this study is to investigate the factors that play a role in the adoption and development of E-Commerce and, hence, develop strategies that conceptualize the influential factors that form as enablers and disablers of E-Commerce. In this paper we provide some answers about the current situation of e-commerce think later on prospects that will enable the benefits from all the advantages offered by this new mode of trade. This paper is organized as follows. Firstly, a concept of e-commerce is briefly introduced, followed by the construction of the research model, including all the aspects of e-commerce that are the object of our investigation. Finally, implications drawn on the study results and analysis are discussed, followed by the research limitations and a conclusion.
2. Understanding the Concept of E-Commerce
Information and communication technology (ICT) is radically transforming the way individuals, organizations, and governments work. The internet in today’s information societies has become an essential channel that is used for dissemination of information, products, and services. People prefer to use the internet as a transaction tool in different areas, such as, learning, shopping, marketing, travel, trading, etc. Carter and Belanger (2003) emphasized the use of ICT to improve efficiency and access to government services across all stakeholders in G2C, G2E, G2G and G2B services. Additionally, governments have realized the importance of the internet and have undertaken critical transformations to use it to deliver public services, so that citizens can always access them regardless of their location (Abdulkarim, 2003). Fang (2002) has described e-government (part of e-commerce) as a method for governments to use the most innovative ICT services, particularly web-based internet applications. These applications are able to provide citizens and businesses with more convenient access to government information and services, to improve the quality of services and provide more opportunities for democratic institutions and processes. E-Commerce involves many issues such as trust, security, privacy, accessibility, familiarity, awareness, and quality of public services (Jaeger, 2003).
For instance, the rapid growth of E-Commerce initiatives in the MENA (Middle East and North Africa) region reflects its compelling advantages, such as enhanced governmental performance, lower cost structure, greater flexibility, broader scale and scope of services, greater transparency, accountability, and faster transactions. However, getting people to be continually engaged in e-commerce services is a challenge since only with a few mouse clicks they will be moved away. An agreement seems to enhance better customer service and its consequent effect on online satisfaction and reuse. Especially, online satisfaction is not the only primary driver of online customers’ continuous behavior, but also the key to building and retaining a loyal base of long-term customers. Many institutions, such as the World Bank, the United Nations, Europe’s Information Society DG, the Canadian Common Measurement Tool (CMT) of satisfaction, the European Customer Satisfaction Index and the American Customer Satisfaction Index, evaluate e-commerce progress and satisfaction using various methods and indices (Fitsilis, Anthopoulos, &Gerogiannis, 2010). factors influencing e-commerce
Businesses implementing E-Commerce in developing countries face substantially greater challenges than businesses in developed countries due to the unreliability of the internet connection, the poor availability of accessing it due to the poor infrastructure, the high cost of doing so, and also the low level of ICT penetration throughout the country (Molla and Licker, 2005b; Molla and Licker, 2005a). Aleid (2009) carried out an investigation of different E-Commerce schemes in a number of countries with regard to culture, infrastructure and human behavior. They find that there are a number of factors that may inhibit the diffusion of E-Commerce into developing countries (e.g. infrastructure, security, E-Commerce laws). This study will focus on Developing countries, which is considered to be a marketplace, which is booming for E-Commerce activities in the Middle East (Eid, 2011). Developing countries require further Internet access, exploring opportunities for the Internet in education, government and commerce. However, for these things to be achieved certain requirements need to exist where certain factors play an important role. Next we discuss the most essential factors for the development and effectiveness of e-commerce. factors influencing e-commerce
3. Key Factors Impacting Ecommerce
Johnson-George and Swap (1982: 1306) asserted that “willingness to take risks may be one of the few characteristics common to all trust situations.” Kee and Knox (1970) argued that to appropriately study trust there must be some meaningful incentives at stake and that the trustor must be cognizant of the risk involved. The definition of trust proposed in this research is the willingness of a party to be vulnerable to the actions of another party based on the expectation that the other will perform a particular action important to the trustor, irrespective of the ability to monitor or control that other party (Park and Kim, 2003). Trust can be a vital factor in business to consumer (B2C) E-Commerce. It gives consumers faith to buy products or services even if an e-trader is unknown. It encourages more use of E-Commerce technologies, makes the e-transaction process easier, enhances the level of acceptance and adoption of E-Commerce, leads to the improvement of consumer commitment, raise customer satisfaction, introduces the concept of loyalty, sustains long-term relationships with customers and assists the acquiring of a competitive benefit. Future purchases can be motivated and increased prices tolerated. It reduces customer worries about information privacy, and helps customers to tolerate the irregular mistakes made by the e-trader (Pittayachawan, 2008). Trust is a complicated concept and has a multitude of sides to be addressed. There are a number of researchers who have continually approached the ‘trust’ issue from a technical side such as Internet and network security and even web interface design (Fernandes, 2001; Clifford et al., 1998; Pittayachawan, 2008). Nonetheless, according to Klang (2001) and Ratnasingham and Kumar (2000), considering just the technical perceptions will not guarantee trust in e-commerce.
It is widely acknowledged by both government and industrial organizations that, from a consumer point of view, issues of information security are a major obstacle to the growth of E-Commerce. The perception of risk regarding Internet security has also been recognized as a concern for both experienced and inexperienced users of Internet technologies (Miyazaki and Fernandez, 2001). Furthermore, Miyazaki and Fernandez (2001) have identified the fraudulent behavior by online retailers as a key concern for Internet users and, therefore, E-Commerce users Rose et al. (1999) identifies hackers as an obvious security threat to E-Commerce.
This happens because the online availability and accessibility of the stored data of many corporations gives any hacker on the Internet the chance to steal data from these corporate databases. These threats have been identified in several new studies (Aleid et al., 2009; Al-Ghaith et al., 2010). Dixit and Datta (2010) studied the acceptance of e-banking among adult customers in India. The findings depicted that many factors like security and privacy, trust, innovativeness, familiarity, and awareness level increase the acceptance of e-banking services among Indian customers.
Awareness and Perceived Usefulness
Within the context of the information systems (IS) domain, much research has outlined the significance of the influence of perceived usefulness on attitude towards the use of e-commerce.
The real reason why customers would use E-Commerce is that they find it a useful facility for conducting shopping online (Alghamdi, 2011). Furthermore, according to Sathye’s (1999) research, the use of online banking services, which is a good example of e-commerce, is new knowledge to many customers, and the lack of awareness of online banking is a crucial factor in preventing customers from adopting it. In his study of 500 Australian customers, he concluded that customers were not aware of the potential benefits of online banking. This was supported by another study by Howcroft et al., (2002) in which they found that the issue of lack of awareness and knowledge of online banking services contributes e-commerce adoption challenges. Suki and Ramayah (2010) studied user acceptance of the e-Government services in Malaysia. Their results indicate that the important determinants of user acceptance of the e-Government services are perceived usefulness, ease of use, compatibility, interpersonal influence, external influence, self-efficacy, facilitating conditions, attitude, subjective norms, perceived behavioral control, and intention to use e-Government services/system.
As the internet is fast becoming a major source of information and services, a well-designed e-commerce website has become essential so that citizens can access public information and improve their participation. E-commerce websites can serve as a tool for both communication and relations for the customers and general public. Information and data can easily be shared with and transferred to external stakeholder (Moon, 2002). Henry (2006) defines web accessibility as getting people to use, perceive, understand, direct and interact with the web. The International Standards Organizations (ISO) has defined accessibility as “the usability of a product, service, environment or facility by people with the widest range of capabilities”.
Gummerus et al. (2004) define the user interface as the channel through which customers are in contact with the e-service provider. Park and Kim (2003) found that the quality of the user interface affects customer satisfaction directly, since it provides physical evidence of the service provider’s competence as well as facilitating effortless use of the service. Because of its importance to customer satisfaction, Tan, Tung, and Xu (2009) identified fourteen key factors for developing effective B2C e-commerce websites. Also, Cyr (2008) investigated the effect of B2C e-commerce website user interface design factors (such as information design, navigation design, and visual design) on trust and satisfaction across three developed countries; Canada, Germany, and China. Cyr found that these user interface design variables are key antecedents to website trust and website satisfaction across cultures.
The perceived quality of a service has two dimensions; the technological dimension, which refers to what is delivered, and the functional dimension, which refers to how the service is delivered. Speed of response, offer updates, and site effectiveness, refers to the technical quality (Rust & Lemon, 2009). Interactive communication, personalization of the communication and of the service, as well as new forms of customer access refers to the functional aspect of quality. Product/service quality is defined as the customer perception of the quality of information about the product/service that is provided by a website (Park & Kim, 2003). According to Mcknightetal., 2002, website content quality has been argued to be an antecedent of online customer trust on quality. In addition, Park and Kim (2003) found that the information quality affects customer satisfaction directly. Karunasena and Deng (2012) have identified the critical factors for evaluating the public value of e-Government in Sri Lanka. The study showed that the deliveries of quality information and services, user-orientation of information and services, efficiency and responsiveness of public organizations and contributions of public organizations to the environmental sustainability are the critical factors for evaluating the public value of e-Government in Sri Lanka.
The government’s role in developing countries as an important one that facilitates the essential requirements for the development of E-Commerce such as providing robust secure online payment options, ensuring a solid ICT infrastructure, providing educational programs and building up awareness using different means such as media and education institutions. The results of their study show the significance of government promotion and support as a crucial factor (AlGhamdi et al., 2011). According to Molla and Licker (2005), state that the government demonstrates strong commitment to promoting E-Commerce. In Saudi Arabia, Eid (2011) posit in his study that the Saudi Government’s support was recognized as an important element in the development and growth of local E-Commerce. According to Eid’s study, some Saudi citizens believe in the importance of the government’s role. Interviewee 8 commented on the diffusion of E-Commerce by government and private accreditation in providing the basic facilities such as a house address for every citizen, to be used online for accurate delivery of products and documents and special services. If there is no reliable postal service, there will be no e-government. factors influencing e-commerce
4. Constructing a Research Model
The development of E-Commerce in this research is measured along the four facets stipulated in the diagram below. This study allows the researcher to discover general attitudes and perception that people have on personal, technological and transactional levels. To determine the connection and effects these attitudes have on e-commerce is paramount to developing e-commerce. The facets surrounding this study revolve on the following;
Security and privacy: the perception of e-commerce portals as secure platforms without any uncertainty and adverse consequences after e-commerce use, and the ability to determine when and what extent information about them is communicated to others for maintaining confidentiality.
Trust and Loyalty: the willingness of people to rely on and willingness to frequently use e-commerce portals for conducting transactions based on the feelings of confidence and assurance.
Accessibility and Awareness: the perception of user interface quality and the degree of awareness on information about products and services delivered from conducting transactions from any location at any time through e-commerce portals. factors influencing e-commerce
Quality and benefits: the perception of quality of products and services offered from e-commerce portals and benefits that arose from conducting such transactions.
Figure 1: The Research Model
5. Implications for Ecommerce in Developing Countries
In developing countries, IT and communication or rather e-commerce growth are substantial. Technology effectiveness is essential in E-Commerce success. However, human, economic, and other organizational issues must be taken into account as well. In this study, we evaluated the current status of E-Commerce in Developing countries. The evaluation of current status reveals opportunities that should be seriously tackled by organizations, if they are to survive the consequences of globalization and open markets. There should be an immediate implementation of a governmental infrastructure to support e-commerce. This thesis explored the areas enabling and huddles to the development of e-commerce. Online consumers face problems concerning security and privacy. They are exposed with online risk such as hacker mischiefs. Moreover, when buyers make payment using credit cards, they are exposing their banking information which could also be manipulated by hackers. The results of this research showed that majority of the respondents felt that internet shopping is risky due to the same reason. Amongst the perceived risks is financial, product performance, social, psychological and time convenience loss. Other than stolen credit card information, there are also risks in delivery. The time taken for delivery may take quite some time, therefore, anything could happen in the process of delivery. Buyers may lose the item. Online vendors might not be responsible for the loss and this leaves the buyers to bear all the consequence. When the perceived risk is greater, the relationship between intention and online purchasing will be weakened. factors influencing e-commerce
The implementation of an effective Internet e-commerce solution in Developing countries or other country that want to develop its e-commerce system can consider the following key steps: Developing strategy; before implementing Internet e-commerce, an organization must clearly define its goals. Many companies create goals that are not measurable or specific. Assessing readiness; before taking on the complexities (and risks) associated with implementing Internet e-commerce, an organization and its management should take stock of their current systems and capabilities. Four key drivers predict an enterprise’s ability to succeed in e-commerce. These four drivers are: leadership; governance; competencies; and technology.Designing the project; Although projects will differ greatly in the details, there are some common requirements for implementing Internet e-commerce, including: managing the project, developing an outsourcing strategy, selecting an Internet service provider, selecting e-commerce service providers; and designing website security. Integrating the solution; In developing an Internet e-commerce platform, an organization must also consider how to integrate its e-commerce applications with its other business processes. For example, the richness of corporate intranet applications positively affects e-commerce capabilities. Extending intranet applications into the Internet permits an organization to provide more value to customers in several ways: real-time access to information; and ability to perform business transactions. Measuring effectiveness: Given the major investment that implementing e-commerce entails, it is only common sense to measure the return. Successful e-commerce companies have serious and accountable metrics and clear agreements about using them across the organization. It is in the appropriateness and completeness of the metrics selected that typically set successful e-commerce implementations apart from the ones that are unsuccessful.
Under the guidance of grounded theory and through analyzing and synthesizing the gathered data, a content analysis of e-commerce enablers and disablers in developing countries was constructed.
This research highlights the most important factors that need to be considered in order to support the proliferation and advancement of e-commerce. Countries need to encourage and improve the e-commerce developments. This research sheds light on the potential factors that may play a significant role in supporting the proliferation and advancement of E-Commerce in developing countries. The outcomes of this study may contribute to the market stakeholders’ understanding of their potential customers’ needs and current concerns. Exploring the market, especially at this time while e-commerce is still in its development stage, is critical for industry stakeholders in order to ensure the success of this emerging market. Future research should focus on studying the development of e-commerce and testing the research model. Consequently, potentially important dimensions of the study could include an investigation in multiple cities, and especially in more rural areas, which may lead to more accurate and comprehensive results and analysis. Also, comparative research in different parts of the world would produce more complete findings. The results of this study could then be compared with those of other developing countries having similar conditions to see if there is a significant difference.
Key takeaway
- The availability and continued growth of Internet technologies (IT) have created great opportunities for users all over the globe to benefit from IT services and use them in a variety of different ways. The use of IT to conduct business online is known as Electronic Commerce (E-Commerce).
- We are witnessing a boom of new technologies, especially in the service sector (IT, Telecommunications, Internet, etc.). Due to technological advances economic transactions have become much easier and faster and this is mainly because of the development of e-commerce. Real engine of the new economy, e-commerce is a remarkable source of competitive advantage for businesses and a new space for consumers. In the coming years, growth and profitability will depend most likely the ability to introduce these new emerging technologies and adopt new methods of business transactions. Since many years ago computers, appliances, plane tickets and many other items are available for purchase on the Internet using cards issued by local banks. Although this technological trend could significantly strengthen the national economic structure, its role and place in developing countries economic structure remains unclear and leaves many questions to ask:
Most people have wondered how new online stores are able to offer the variety of inventory that is needed to compete with established brick and mortar outlets, and the e-commerce vendor is at the heart of that answer. E-commerce vendors are needed to supply the software and services used to start and operate most online stores. However, they are more prominently known for supplying consumable and durable goods to online shop owners so that they can resell the items at a profit. As many people realize their dreams of store ownership by opening their own electronic retail stores, there is an increase in the need for suppliers for this fast paced niche sector within the retail industry. E-commerce store owners must choose suppliers that are agile, flexible and quality oriented, or they risk being driven out of business by competing e-shops that have leaner, more reliable supply chains.
One of the most exciting ways that online stores can get up and running very quickly and with plenty of product offerings is by using drop shipping vendors, according to Practical eCommerce. These vendors allow retailers to take orders from customers over their websites, and the vendors deliver the products directly to the purchaser. It sounds very easy, but there are some drawbacks. For instance, the online retailer must rely on the drop shipper to make appropriate deliveries of undamaged products to their customers within specified time periods. Since the vendors have many different customers, there are bound to be mistakes. The online retailer must be ready to field customer complaints when this happens. Also, the profit margins on the drop shipped items are low because the e-commerce vendors are doing most of the logistical work and inventory storage. The wholesaler is another type e-commerce vendor. Online store owners can purchase items from wholesalers that are below list prices and resell them to their online customers for a profit. Even though higher shipping costs are involved, the profit margins that online retailers gain by using overseas wholesale suppliers are almost always larger than when they use domestic wholesalers. However, online retailers must watch for quality issues when using overseas supply companies that beat out the competition through the use of cheap labor. Online retail business owners who sell specialty goods often find that the best e-commerce vendors are the manufacturers of the goods. These e-shop owners can establish purchase agreements with manufacturers, and the results are lower prices and potentially higher profits from sales.
Characteristics of Reliable E-Commerce Vendors
Reliable e-commerce vendors have quality control systems in place to ensure that purchased products are delivered without damage. The best way for online retailers to find out about the quality control practices of potential e-commerce vendors is to go through a company that pre-screens vendors. The pre-screening service helps to reduce the chances of retailers falling prey to scam artists, and they often highlight their quality control practices and past performance. Reliable e-commerce vendors also work with retailers to solve unexpected problems instead of leaving the online retailer to handle customer care nightmares on their own. Retailers can get good indicators of the quality of the vendors’ services by checking if near competitors or leaders in the market are being supplied by them. If market leaders have been serviced by the vendor for a long period of time, then the vendor probably has a sustainable track record for success.
Maintaining Good Retailer Vendor Relationships
Success with e-commerce vendors takes work just like all business and personal relationships. Online retailers can establish trust with their vendors by maintaining good payment histories. They can continue building lasting business partnerships by deviating as little as possible from their vendors’ ordering systems as possible; if the vendors have many customers, they probably do not want to waste time processing orders that do not fit their predetermined formats. Making friends with vendors is a definite positive, as it becomes easier to educate them about one’s unique product requirements; for example, vendors might be willing to go the extra mile for a friend as opposed to someone who just places online orders from them.
Conclusion
Vendors for e-commerce retail sites have become key elements of the supply chain for many business owners. Depending on the type of products sourced and the number of customers that the vendor supplies, the process of providing the appropriate products at the right time can get complicated. Subsequently, online retailers realize that the same tried and true principles of supply chain management are applicable when doing business with an e-commerce vendor as they are when applied to a traditional supplier.
Key takeaway
- Most people have wondered how new online stores are able to offer the variety of inventory that is needed to compete with established brick and mortar outlets, and the e-commerce vendor is at the heart of that answer. E-commerce vendors are needed to supply the software and services used to start and operate most online stores.
- However, they are more prominently known for supplying consumable and durable goods to online shop owners so that they can resell the items at a profit. As many people realize their dreams of store ownership by opening their own electronic retail stores, there is an increase in the need for suppliers for this fast paced niche sector within the retail industry.
- E-commerce store owners must choose suppliers that are agile, flexible and quality oriented, or they risk being driven out of business by competing e-shops that have leaner, more reliable supply chains.
Planning, designing, and scheduling are the primary and crucial stages of any business practice; either it is an offline or online business. Outlining of the ecommerce website will help you to jump on to the originality regarding user experiences and product value in the market rather than imaginations.
Well, if you are willing to start ecommerce website then surely you need to hire ecommerce website developers. Make sure that hired fellows have enough technical knowledge regarding the different phases of ecommerce website development such as planning, research, designing and launching.
Below are some essential stages of ecommerce development which are certainly required for any successful ecommerce website:
The ecommerce website should be designed in a way that the candid interactions can be done between the professional ecommerce website Development Company and users. Hence, agendas of website development company should be well-understood by the website designers. To meet this need, the frequent conversation is necessary between website designers and company developers.
This will help to estimate the round figure of users and determine the breakthrough keywords by which the audience will explore your ecommerce website development company. This is the most efficient way to fascinate more right users rather than expending money on marketing strategies.
2. Preparation of Website Outline
This step is one of the crucial stages of e-commerce development. It includes considering the needs of ecommerce Website Company and the users and making efforts to meet them bit by bit.
Consider yourself as a user for a moment and try to cover all the requirements of your clients such as content, search and landing pages. This will also give the idea of crucial information which you should add up on your website to convince your users.
Moreover, this will give you the exact idea of how the customers approach your website and how much time they spend on your website. Moreover, it will also enable the information regarding visited pages of your website by the customers.
The information texture will reflect outlines of your ecommerce website. This will be the core portion of your website as people visit your website quickly if they will find what they are looking for. Hence, you should adopt some effective information practices to portray your product in well-organized and well-defined manner. All in all, as your website accessible and informative as the users, will visit and become your customers.
This stage is formed to appeal the customers using a graphic representation of your ecommerce website. This stage needs lots of creations and animations for the display of knowledge and detailed information regarding your ecommerce company and product.
Using different software, the prospector of your company will be designed. These templates contain the information regarding company’s agenda, strategy, principles, and products. It also covers the ecommerce website development services which company offers to the users. Moreover, your company’s fame and success will be represented in the form of videos or images.
This is the backbone of any ecommerce website. This process includes user, server-side applications such as CGI scripts, incorporation of third party tools and solutions, which will enable more accessibility of your ecommerce website.
Moreover, third party tools, server-side applications, and few essential elements collectively function well and make the number of users of the ecommerce website. You can simply compare the construction procedure with the building framework and web designing with the walls.
Hence, website construction is a crucial portion of the ecommerce website development. So adoption of effective web construction practices will be helpful to strengthen the other elements of website developing.
It is the last and essential step of the ecommerce website developing. This is the stage when you shift your website from the development server to the launching mode. It is also the time to re-check each and every content of your website.
Moreover, the reassessment of the information should be done, which is displayed on the website regarding your brand and product. However, the reassessment of website elements is necessary for all the stages of ecommerce website development.
Development of ecommerce website needs correct research about the product and ecommerce website owners. Moreover, adoption of effective practices such as the use of client-oriented applications, animations, display of owner’s success oriented images will be handy for enhancing the users and clients.
You should make sure that your website is easily accessible for the users. The frequent conversation between website owner or partners and the hired website developers is essential to design the ecommerce website as per the requirements of owners and users. After finishing the web design, launching of the website takes place. Hence, the journey of ecommerce website gets started.
Key takeaway
- Planning, designing, and scheduling are the primary and crucial stages of any business practice; either it is an offline or online business. Outlining of the ecommerce website will help you to jump on to the originality regarding user experiences and product value in the market rather than imaginations.
- Well, if you are willing to start ecommerce website then surely you need to hire ecommerce website developers. Make sure that hired fellows have enough technical knowledge regarding the different phases of ecommerce website development such as planning, research, designing and launching.
Business development is a somewhat-ambiguous term with a function and responsibility that varies from company to company.
While the definition has been endlessly debated, the ultimate goal of business development is to find strategic opportunities that create long-term value. This requires effort from brand marketing, sales, partnerships, and ultimately depends on the delivery of quality products to match these efforts. Essentially, BD applies to every area of a company.
Business development is often used interchangeably with sales, which underestimates the many other considerations necessary to execute on strategic business initiatives. While sales is an important component of BD, it's one of several key factors that go into creating value for a business.
The broad definition of business development underlies just how crucial it is to success in any industry, and ecommerce is no different.
Business development is built on relationships
Through its varied applications, every area of business development has one thing in common: it depends on building relationships - with customers, partners, and departments within a company. Every company relies on other organizations and all of its departments to get their product or service to a customer, and building strong business relationships is necessary to succeed in any field.
Consider a pro football team: its objective is to win games and increase profits. But to achieve that, the coach needs to be in sync with the players, general manager (chooses players and oversees budget), training staff (monitors player health), PR (manage distractions), and owner (verifies expenses), who all play an integral role in building a profitable championship team. With a unified front established, the team can then work efficiently with third party contractors and organizations to fulfill all outstanding needs.
Much like the above example, it's important for an ecommerce company to establish clear objectives that are translated into goals for each department. A target market must be established to select the right products for a determined audience, and brand messaging should reflect these principles. A healthy line of communication between departments ensures that individual objectives are aligned to meet company goals; from there, each team works to forge additional strategic partnerships to reach their targets.
What is business development for ecommerce?
Once goals are set and each department knows what it needs to do, an ecommerce business inherently relies on other organizations to complete every step necessary to get the product to customers. While every company has its own unique BD needs, common business relationships include:
- Shipping: Reliable and timely deliveries are necessary to keep customers happy, and this depends in great deal on the shipping provider. An online store must be responsible for a shipping provider's fulfillment regardless of fault, making this an extremely vital partnership. Factor in the cost and corresponding economic implications, and this is an alliance that can make or break an online store.
- Supply: Product fulfillment depends just as much on suppliers as it does on shipping. Being in sync with a supplier is crucial to maintaining inventory, keeping the promise to customers, and scaling your business.
- Marketing and advertising: Effective digital marketing is quite work-intensive, which is why many ecommerce businesses seek outside help for SEO, PPC, email marketing, and display advertising. Another important consideration is content marketing, which requires both quality curation and strategic distribution to be successful.
- Product: Offering products to complement your main offerings--accessories--helps fulfill customer needs and increase retention. When you can't get these from a primary supplier, it can be accomplished by direct partnerships with manufacturers.
- Customer service & PR: Perception is reality, especially in the online marketplace where one bad review can preemptively end your relationship with a customer. Established enterprises often partner with PR agencies to generate positive press and manage negative publicity. One of the best ways to ensure customers stay happy? Excellent customer service. This often requires an additional partnership, whether with live chat software, a help desk application, or a third-party call center.
Key takeaway
- Business development is a somewhat-ambiguous term with a function and responsibility that varies from company to company.
- While the definition has been endlessly debated, the ultimate goal of business development is to find strategic opportunities that create long-term value. This requires effort from brand marketing, sales, partnerships, and ultimately depends on the delivery of quality products to match these efforts. Essentially, BD applies to every area of a company.
- Business development is often used interchangeably with sales, which underestimates the many other considerations necessary to execute on strategic business initiatives. While sales is an important component of BD, it's one of several key factors that go into creating value for a business.
- The broad definition of business development underlies just how crucial it is to success in any industry, and ecommerce is no different.
A Business Case can be a powerful tool in obtaining the funds you need to drive change in achieving optimally performing systems. We explore 9 common components of a well written proposal.
Navigating the world of submissions and proposals can sometimes feel like a juggling act. With your day to day workload and an ever changing industry it may be difficult to secure capital for investments to return long term benefits.
Although procurement of funds for requirements such as preventative maintenance may be easier to obtain through OPEX, the focus has traditionally been on short term benefits. Whereas in the longer term, capital investment can provide performance and economic benefits that outweigh short term gains.
While maintenance is a necessary ongoing cost, advancements in technology such as fault detection, isolation and restoration offer the possibility of reliability improvements for larger and longer-term benefits to utilities and consumers.
Maximise the impact of your business case with these key elements:
An executive summary should provide the following:
- A brief snapshot of the problem that you are addressing
- An overview of possible solutions to achieve cost and performance benefits
- Include contributors and people that you have consulted to reflect internal support and provide the decision maker with further confidence in your Business Case
Be aware of your organisation’s overall strategy and goals. If your proposal is counter intuitive to these goals gaining approval for funds can become more difficult. Keeping in line with your organisation’s strategy shows a clear path to how your project can help the business achieve its targets.
It is important to have an understanding of whether or not your Business Case requires a philosophy shift in the way your organisation is structured and/or operated. Taking into account a broader view that looks at the ripple effect outside of the short term expense of your project can add more credibility and substance to your proposal, as well as assist in understanding where change is needed.
A concise and informative project outline based on reliable data can add weight to your Business Case. These fundamentals will help the reviewer gain a better understanding of your proposal:
- Clearly state why you are proposing the project, making sure business needs are addressed
- Include a clear analysis of the problem
- If reviewers fail to understand the problem they will not connect to why resolving it is necessary, which in turn can limit the success of your Business Case.
- Provide data that shows urgency of the problem
- Define what areas of the business are being affected
- Include options to resolve the problem and relate the remaining sections of the proposal to these options
- If you are including a status quo option, one that requires no change from the current situation, it is important to address the impact of doing so, especially in terms of how it will or will not address the problem being faced
- Include details of alternate timelines if the options have different schedules2
- Reference industry standards and guidelines that your project aligns with as this can have a positive effect on cost savings
- Utilise visual tools where necessary to ensure the project will be clearly understood
A detailed timeline and strategic plan should cover:
- How you will achieve the desired outcome including key milestones and significant deliverables2
- What resources will be required
- Clear indication of the required roles and responsibilities
- How the project will be monitored and what Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) will be implemented to ensure targets will be achieved at the various stages
- Whether your plan will have an impact on existing organisational events such as shutdowns, corporate, operational and/or structural changes. It is also worth noting if such events will have an effect on your project.
Benefits can be defined as detail savings in terms of revenue and productivity that are a result of achieving greater efficiency.2 An effective representation of benefits typically includes:
- Measurable financial benefits which will be used later for comparison against costs to reflect the actual Return on Investment (ROI)
- Societal impacts such as increased staff morale or consumer satisfaction can be included but should not be the primary focus
- Detailed information on the source of your data and assumptions regarding calculations adds further credibility to your proposal.
It is critical to cover all potential risks as decision makers will be looking for analysis that includes:
- Risks associated with the problem and the likelihood of these occurring in easy to define terms, i.e. low, medium, high
- Consideration of threats and opportunities that can inhibit or maximise return from the project
- Risks related to proceeding or not proceeding with the proposal
- Specific risks linked to the various options presented
For a comprehensive proposal it is imperative to ensure all costs are detailed clearly and concisely. Quantifiable costs relating to CAPEX can be categorised into one or more of the following:
- Reliability
- Security
- Efficiency
- Performance Improvement
- Safety
Non-quantifiable costs such as credibility and reputation should be acknowledged ideally in terms of how they impact quantifiable costs and benefits.
Present your final recommendation and why you have come to this conclusion. Highlight the benefits and costs involved, and ensure the recommended solution clearly shows the greatest ROI. Easy to understand formats such as tables are powerful tools in relaying your point to the reviewer. As most of the detail has already been covered, you can present this information in a summary format.
The concluding summary is your opportunity to emphasise the crucial parts of your Business Case that you want decision makers to remember. It should include:
- The problem and business need - why you are putting forward your Business Case
- Benefits and risks of the options - solutions to the problem
- Return on investment - what the overall gain will be to the business
- Final recommendation - based on the information presented
Key takeaway
- A Business Case can be a powerful tool in obtaining the funds you need to drive change in achieving optimally performing systems. We explore 9 common components of a well written proposal.
- Navigating the world of submissions and proposals can sometimes feel like a juggling act. With your day to day workload and an ever changing industry it may be difficult to secure capital for investments to return long term benefits.
- Although procurement of funds for requirements such as preventative maintenance may be easier to obtain through OPEX, the focus has traditionally been on short term benefits. Whereas in the longer term, capital investment can provide performance and economic benefits that outweigh short term gains.
The number of people shopping online is increasing day by day as it is convenient to do so from anywhere. If you have a physical store, you should consider building an online store too, as it is a great way to make extra money. Also, having e-commerce solutions for your business is a smart and cheap way to reach the global audience.
The development process of an online/e-commerce store is hard if you have no clue where to start. But the good news is that to build a good custom e-commerce site doesn’t require much money, time or technical knowledge.
With the right knowledge of e-commerce platforms like Shopify, Wix, and BigCommerce, you can quickly develop your online site. You can even hire an e-commerce website development company for creating your website. All these platforms are easy and cheap to use whether you use it to develop yourself or hire an ecommerce web development company.
There is no coding required, but you do need to a full guide about how to use these tools for developing your online store. It is exactly what we will do in this blog.
The 11 steps that will guide to develop an e-commerce website
1. Find the website builder that fits your needs
There are numerous ecommerce platforms available in the markets that are easy to use. Some of the tools are expensive while others are affordable. So, let’s list some of the best tools and their features for your online store development.
- Shopify
The best ecommerce development platform is Shopify. It has tons of features that will help you develop a scalable online store. It has the ability to sell products across many social platforms like Facebook, Amazon and so on.
- Wix
Wix is best suited for small businesses and startups. It has more than 510 templates that suit all genres of business like sports, beauty and so on. All the templates are optimized for mobile use. Other features include adding product videos, editor and easy user-interface.
- BigCommerce
Another great platform for your eCommerce site is BigCommerce. It creates a scalable site and has great SEO tools and has many more features than its competitors.
- Weebly
With plenty of features with drag and drop being one of them, it is the easiest platform. The best feature of Weebly is that it lets you create dedicated pages for all your products.
- Magento
The current favorite tool for developing online store is Magento. All over the globe, the developer prefers it. It integrates advertisement, analytics, and content creation and so on to provide the best user experience.
Some other eCommerce website development platforms are- WordPress, Big Cartel and so on.
Why to use these tools for building your online site?
A developer can make a website from scratch using coding and programming. It will take time, but the end result is great. So, why use these tools?
- These website building tools host your site on the internet.
- It aids you in buying a domain name.
- They are secure and have certificates to prove that. It helps to keep the payment getaway and customer details safe.
- It monitors your site continuously so that it runs smoothly.
Now, you must be confused about choosing the right platform. Don’t, check with your team and find out the purpose of your online store. Once you are clear on that, the right platform will be easier to find.
2. Test the tool
Before you start with the development process, test the tool to find out any discrepancies. For a successful online store, this step is crucial. To test the e-commerce development platform, all you have to do is sign-up for the free trial and start exploring.
Here some things to check in the test which will help you find the right tool:
- How easy is it to customize the features or modify it?
- Are the templates/theme provided suits your business? Also, check whether it’s easy to choose them or not.
- How is the navigation feature and can you customize it to add sub-menus and all?
You can make a trial site and check out all these and other things that you require for your business.
3. Buy the right plan for your business
Once you have finalized your e-commerce site development platforms and tested it. It’s time to choose a plan for starting the development process. All these tools come with many plans- free, paid version for individual and paid version for companies.
According to your need and size of the online store, you will have to choose the plan. A free plan of all these platforms supports minimum selling of products and runs up to 15 days.
If you want to build an e-commerce store, you need more features, and functionalities, which mean buying the full version. If you want a small online store, maybe you can develop it using the free version.
4. Register for a domain name
A domain name is the part of URL that has the name of your business. It is crucial to have a good domain name as it builds trust and brand with your consumer. With the help Shopify, Wix and BigCommerce platform, you can buy a great domain name in around $10-$20 per year.
Here are some tricks and tips to select a correct domain name for your eCommerce solution:
- Country code: Picking a correct country code is crucial. If you plan to sell your product to only international clients, use a dot com (.com) domain. If selling to a specific county, then you can use their code. Like Amazon has both .com for US and international consumers and .in for selling just in India.
- No brand name: Avoid using brand or product name in the URL as it can get you into legal troubles.
- Unique: The domain name should be unique, but not so weird that people find it hard to look on a search engine.
- Integrate a keyword: In the domain name, add a term that resonates with your business. The keyword will help you to have a higher rank in search engines which will ultimately get you more traffic and sales.
If you already have a domain name, you can link it with your online store or cancel that agreement.
5. Pick template for your website
Templates also known as themes make your site appealing. Most e-commerce platform lets you design and develop your own site too, but that requires coding. So, if you want to avoid that, use these templates.
Here are some tips for choosing the right template:
- Features you want in your store: Features are the key to a good website. So, brainstorm and decide which feature is more important for your store. It can be mapped, about us page and so on. Make a list of features and use it narrow down the template.
- Homepage style: Homepage is the first thing consumers will notice about your e-commerce site. So, make sure that the chosen template does justice to it. Based on your business goals, decide what you want more videos, sliders, single image and so on.
- Smooth navigation: The navigation of the website should be simple and helpful. A potential customer will surf through the site for 10-20 seconds if the template’s navigation feature is weak; it means that they won’t find what they are looking for easily. It will amplify bounce rate of the website.
Other than that, check out the font and color of the template. It should go with your brand image and should not be offensive.
6. Customizing the template
After choosing the template, the e-commerce development tools allow the user to customize it. For customization, you will have to go to the store’s admin panel. You can modify anything according to your will.
- Text Size, Color and Font
- Color of the theme
- Use of images
- Product’s position and so on.
7. Time to add the products
Once you have customized your template, it’s now time to add products to your website. There is a button that will guide in adding your products. You must add these details to your product to make it more alluring consumers:
- Name of the product and name of the brand (If outsourcing)
- Price of the good
- Category
- Weight for physical things
- File (For eBooks and all)
All the platforms have a different policy when it comes to a number of products, product description and variation you can add.
A product description is crucial to get the attention of the consumer along with images and category.
Check out these pro tips for the description:
- Don’t use a long sentence to describe the product. No one has that much time.
- Don’t use cliques or technical jargon while describing a product.
- The description should also be SEO optimized as it will help you rank higher and get more traffic and sales.
For product image:
- The images used should be high in quality and must not be blurry.
- The size of every image must be the same.
- The photos of the product should be taken with a piece of good quality equipment.
- The image should be visible from every angle, so a 360-degree option is necessary.
- The image should have a zoom button.
- The images used should be optimized so that they don’t slow down your website’s speed.
For product category:
- Price range so that people pick products that they can afford.
- Option to filter the product using price, size and so on.
8. Payment methods
Online stores will be incomplete without payment gateway. It is a crucial step in converting a consumer into a buyer. E-commerce development tool makes integrating payment methods of all kinds into the site easy.
They connect the user directly to PayPal, Apple and Google Pay, Credit/Debit cards, Master or Visa Cards for paying. The option to pay on delivery is also available.
Payment option:
There are three popular payment options:
- Merchant account and payment gateway: In this option, you partner up with a bank and they accept payment on your behalf. After this, they transfer the amount to your business account.
- Payment gateway packages: In this option, software integrates all the option into one and processes your card payments.
- Credit card payment: In this option, the payment method is integrated with the store’s cart which means you don’t have to leave the site to complete your payment.
Tips to apply the best payment method for your online store:
- To find out which payment methods work for your site, keep these things in mind:
- Figure out the estimated number of total sales
- Customer details are also crucial. Find out, where the customer is from so that you can have a payment getaway preferred by everyone.
- The payment method should also go with your store’s purpose and needs.
Security measures:
Customer worries most about security as they share their private details online. So, making the site secure should be your priority, and it’s also easy to do so.
The website building tools use SSL certificates to secure the website. Secure Socket Layer encrypts user data and optimizes user experience while online shopping secure.
SSL is inbuilt in the tool. If not, it will be available as an add-on.
What is the cost of these Payment Options?
- All the different payment methods have different charges. Since, it comes bundled with other features, de-tangle them. Figure out how much you are paying and for what? Keep the following points in mind:
- You cannot avoid the credit card fee. The provider sets the fee which is passed on by the platform.
- The charge on using payment processors varies from 1%+ 10p to 3% + 30p per transaction.
9. Shipping settings
The next step is to set up the shipping settings so that you can deliver the products on your website.
Different e-commerce platforms have different options, but to set up this tab, you will need these details.
Address of the shipping office:
- Include the address of the shipping origin to calculate taxes and all. It also makes printing labels and asking for quotes easy.
- Address of shipping origin office is required when products are not shipped from the main office.
- Shipping zones you want to cover:
- Shipping rates vary between countries and Zones. All development tools allow the user to charge different rates from consumers based on their zones.
- The admin page shows your shipping zones and the individual rate of shipping for each zone.
- Different shipping options are:
- Here is how you can ship products to different zones:
- Free shipping: If you sell a luxury product and can afford it, this is the best option. Also, set the option of free shipping after a certain value. If your online store sells products that are affordable, then don’t pick this option as it won’t be profitable for you.
- Flat rate: In this option, you use the same amount for shipping any product. It is a great marketing tactic, and you can cover the entire country or some district in one price range.
- Real-time price: The shipping charge depends on the product’s weight, size and so on. It is good for products that are expensive to ship for free.
- Pickup by a customer: A great option is to ask the consumer if they want to pick the parcel from a local store or the office.
Different shipping services:
- The online store building tools allow you to provide different shipping options to your consumers. It includes paying more for a one-day delivery and so on.
10. Settings for the store
Your online store needs to run properly every single minute and this needs proper settings. You can do this by filling out your preferences for each of the following in the store setting section of the tool.
- Language: Select the language that the customer will see on the website
- Currency: The currency you want to deal in
- Time zone: To track the orders, set up your time zone.
- Address: Contact information and address of the main and local office.
- Store Name: Name of the store that you want on the title, homepage and other pages and online searches.
- Contact Details: A public phone number and an email address
- Setting for the order: In this, you set the option of adding tax to your product or not
- Product settings: In the product settings, you can decide what details about the product you want.
You can take help from the tool’s support team to figure out all this.
11. Test the whole site and then publish it
The last step before publishing your site is to test it. You need to make sure that every section of the e-commerce site works perfectly. Any issue can dampen the user experience and sales of your site, so be careful.
Here are things that you should monitor while testing your site:
Checkout process
- Make sure that the checkout process works by making sure:
- All payment methods work against an order
- Shipping charges, price and category, and other details are visible.
- Discount and coupon codes are there or not.
- Whether the taxes on the product is visible or not.
- Refund policy on the product works or not.
- The best way to check all this is by ordering a product and refunding it.
Functionality:
- Make sure all the links and buttons like zoom in button works or not. If any of the functionality of the sites doesn’t work, it will make you lose customers.
- Content:
- Whatever content you use on your online store, should be free of errors and should be original.
- Mobile optimized:
- Make sure that your website works on all mobile devices as people prefer their Smartphone devices more.
- Different browser:
- Make sure that the website is easily accessible on all web browsers. Check the loading time and speed and fix any issue before launching.
Take some time to check these things before launching the site as there is no room for errors in this stiff competition.
Conclusion
The development process of an e-commerce site takes some time and research, but the end-result will be satisfying. With the help of this guide, you can easily use any of the e-commerce website development tools and start creating your online store. Always double check your work and make a detailed plan before executing it.
Key takeaway
- The number of people shopping online is increasing day by day as it is convenient to do so from anywhere. If you have a physical store, you should consider building an online store too, as it is a great way to make extra money. Also, having e-commerce solutions for your business is a smart and cheap way to reach the global audience.
- The development process of an online/e-commerce store is hard if you have no clue where to start. But the good news is that to build a good custom e-commerce site doesn’t require much money, time or technical knowledge.
References
- Computer Fundamentals by: Anita Goel, Pearson Education India ISBN: 9788131742136
- Connecting with Computer Science, by Greg Anderson, David Ferro, Robert Hilton, Course Technology, Cengage Learning,ISBN:9781439080351
- Fundamentals of Computer : For undergraduate courses in commerce and management, ITL Education Solutions Limited, Pearson Education, ISBN:9788131733349
- Introduction to Computer Science, 2/e, ITL Education Solutions Limited, Pearson Education, ISBN:9788131760307
- Frontiers of Electronic Commerce, Ravi Kalakota, Andrew B. Whinston, Pearson Education,ISBN:9788177583922
- Internet: The Complete Reference, Margaret Levine Young, Tata McGraw Hill Education Private Limited, ISBN: 9780070486997
- On the Way to the Web: The Secret History of the Internet and Its Founders, A. Banks,Apress Publication, ISBN: 9781430208693
- Computers and Commerce: A Study of Technology and Management at Eckert-MauchlyComputer Company, Engineering Research Associates, and Remingto, Arthur L. Norberg, MIT Press (MA),ISBN:9780262140904
- Essential of E-commerce technology By V.Rajaraman, Prentice Hall Inida Learning PriviteLimitated ISBN 9788120339378
- E-commerce Fundamental and Application By Henry Chan ,Wiley ISBN:-978126514694
- Information Technology ByDr.KishorJagtap, Tech-Max Publications, Pune