UNIT 3
Techniques of group decision-making
Definition
Decision making refers to the process by which individual selects a particular course of action among several alternatives to produce a desired result. The main purpose of decision making is to direct the resources of the organization towards a future goal and reduce the gap between the actual position and the desired position through effective problem solving and exploiting business opportunities.
Group decision making refers to the process where the group as a whole makes the decision. Group members consider all the possible solution of a problem and select the most feasible option in group decision making.
Group decisions involve transmitting of message between members, and the communication process effectiveness will significantly impact the quality of group decisions.
Techniques
- The Delphi technique - Concerning an issue members with expertise and relevant information are selected to make the decision regarding that issue. Group members are given questionnaires who record their answers in writing. The members do not meet face to face. The replies sent by the group members to the questionnaires are summarized and feedback to them are sent for review. This process is repeated until a satisfactory decision is made.
Advantages
- Ego problems and related issues of face-to-face interaction can be avoided
- Efficient use of expert time
- Avoidance of interpersonal problems
- Enough time is given for reflection and analysis by respondents
- Utmost care can be taken
2. Nominal group techniques - Prior to making a decision, group members have minimal interaction. Steps involved in making nominal group decision making are –
- Group members are brought together and presented with a problem.
- Independently members develop the solutions and write them on cards.
- In a structured format they share their ideas with each other
- during a brief session members ask questions just to get clarifications
- Through a secret ballot group members individually select the best alternative and inform
- The group decision is announced
Advantages
- All members get equal opportunity for participation.
- No member can dominate the discussion.
- Decision can be taken in the right time due to control of time.
- Expertise of each member is used independently.
- Ego problems and interpersonal problems are solved
Disadvantages
- The procedure is too rigid
- Members may be frustrated
- Members cannot have interpersonal relations
- Ideas cannot be cross fertilized
3. Brain storming techniques – This technique is used in group of around eight members sitting around a table in a classroom setting to encourage creative thinking. The success of this technique depends on the members’ ability to listen to others, use this interaction as a stimulus to spark new ideas and feel free to express them. The primary focus of brainstorming techniques is more on generation of ideas rather than evaluation of ideas.
All these ideas are written on the blackboard with a piece of chalk so that everybody can see every idea and try to improve upon them. The leader of the group defines and explains the nature of the problem to the group members and the rules to be followed.
Advantages
- Group members would be enthusiastic, involved immensely and emotional.
- Broader participation of the members.
- High task orientation and also high relation orientation will be maintained.
- Members have a sense of belongingness and the final product is the team effort.
Disadvantages
- Some members may fear that their ideas may be looked down by others.
- Criticism of ideas kills creativity.
- Some people may dominate the process of decision making.
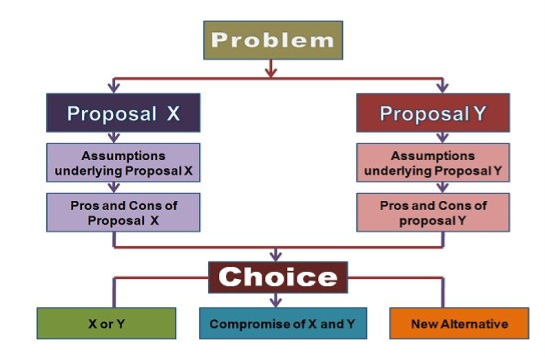
4. Dialectic Decision Methods – The Dialectic Decisions Method is a technique used to overcome the problem in the group-decision making, wherein the group members quickly agree to one alternative proposal and might overlook more promising solutions than the chosen one. Thus, it ensures a full consideration of alternatives.
Flow of dialectic decision making
|
Advantages
- A range of ideas can be exploited.
- Helps focus on critical points.
- Greater number of alternatives.
- Participative decisions.
- Better understanding of final decision.
Disadvantages
- More time consuming.
- Interpersonal conflicts.
- Dominance.
- Everyone cannot express their ideas.
5. Decision tree - In this decision making process alternative solutions are generated. Before ranking the solutions each of these alternative decisions is evaluated. The decision tree is a model in the form of a graphic tool that charts the steps to consider in evaluating each alternative solution in the decision making.
The main points of the decision tree are:
- Using the information acquired in preparing to make the decision.
- Recognizing the sequential nature of the decision making process.
- Decision tree is a graphic outline of the future choices that the decisions made in the present will lead to.
- Decision tree helps managers to evaluate and arrange the information in order and
- Decision tree enables managers to introduce a degree of quantifiability
6. Fish bowling techniques - In this technique, the decision-making group of experts is seated around a circle with a single chair in the center of the circle. One member of the group or the group leader is invited to sit in the center chair and give his view about the problem and his proposition of a solution.
The other group members can ask him questions but there is no irrelevant discussion or cross talk. Once the member in the center chair has finished talking and his viewpoint is fully understood, he leaves the center and joins the group in the circle. Then the second member is called upon to sit in the center chair and give his views in the light of the views expressed earlier. After all experts have expressed their views, the entire groups discuss the various alternatives suggested and pick the one with consensus.
Key takeaways
- Brainstorming is an idea generation process. Under this technique, group members are encouraged to generate ideas to solve the given problems.
- The Nominal Group Process is a technique where goals are set and the problems are identified before the group.
- Delphi technique identify the problem and design a questionnaire for the group members.
Meaning
Committee means a body of persons entrusted with discharging some assigned functions as a group and in a corporate capacity. Committee is a group of persons pooling their thoughts and actions to facilitate the process of decision-making. Alternative names given to committees are boards, task groups, work forces, commissions, councils and-teams.
Definition of E. Dale: “Committee is a group of people (usually not more than four who can sit around a table) which makes decisions or present views points and whose conduct is governed by set of rules”.
A number of persons to take a decision may come together, on some matters decide a course of action, and advise line officers, it is a committee form of organization. It is a method of collective thinking, corporate judgment and common decision. A committee is not a separated type of organization but it is a method of attaching persons or groups to line departments for advice and guidance in business planning and execution.
Essentials
- Define the scope and authority of the committee: The role and authority must be clearly defined and specified for the success of a committee. The purpose of the committee also must be clearly spelled out.
2. Size of the committee: The size of the committee must be small as far as possible. If the size is large, discussions will prolong and committees cannot arrive at decisions in right time.
3. Selection of members: The members of the committee must be selected carefully. They should have possessed knowledge and experience of the topic for discussions. To avoid complexes it is always better to have people of equal status in the committee.
4. Chairman: The chairman of the committee must be well informed of the subject and purpose of the committee. He should give equal opportunity to all members to express their views. He is the guide and leader.
5. Subject Matter: The subject for discussion must be clear. It must also be communicated in advance along with the agenda.
6. Follow up: The minutes of the meetings must be properly recorded, circulated among members for any correction and have the final copy approved by the committee. This will greatly help in the follow up.
Advantages
1. Pooling of Opinions:
The members of committees are from different background and areas of expertise and have different viewpoints and values. Various aspects of the case are highlighted and pros and cons are assessed, when persons with varied abilities sit together and discuss a problem. The pooled opinion will help in taking a realistic view of the problem.
2. Better Co-Ordination:
Committee brings more co-ordination among different segments of the organization when representatives of different departments sit together; the difficulties faced by others are understood and appreciated. This type of frank discussions help on fixing the targets of different departments and better co-ordination is achieved through this type of decision making.
3. Balancing of Views:
The committee helps in balancing the views expressed by different persons. There is a tendency to over emphasize the aspects of one’s own department by ignoring the interdependent character of problems of different departments. A committee helps to bring out an agreed view of the problem by taking into account divergent views expressed in such meetings.
4. Motivation:
The committees consist of managers as well as subordinates. The subordinates view are given recognition and importance. The subordinates are given encouragement and make them feel as an integral part of decision making process. Such committees boost the morale of subordinates and motivate them to improve their performance.
5. Dispersion of Power:
The concentration of power in few persons may lead to misuse of authority and wrong decisions. By spreading powers among committee members this problem can be solved. Committees avoid undue concentration of authority in the hands of an individual or a few.
6. Better Acceptance of Decisions:
The committees taken the decision are better accepted by subordinates. The decisions of an individual may be absolute whereas committees decide in wider perspective of organization. Since the committee represent the various shades of people, these decisions are better accepted.
7. Better Communication:
It is a better form for discussing matters of mutual interest and reaching certain conclusions. These decisions can be properly communicated to subordinates through committee members. The members will transmit correct and authentic information and also convey the background of taking those decisions.
8. Executive Training:
Committees provide a good forum for training executives. They learn the value of interaction, group dynamics and human relations. They are exposed to various view points and learn the art of reaching decisions and solving organisational problems.
Disadvantages
1. Delay:
The main drawback of committee is delay in taking decisions. A lot of time is taken on reaching a decision as number of persons express their view points in meetings. The fixing of committee meetings is also time consuming. An agenda is issued and a convenient date is fixed for the meeting. The decision making process is very slow, thus, many business opportunities may be lost due to delayed decisions.
2. Compromise:
The committee makes efforts to reach consensus decisions. The majority view point is taken as a unanimous decision of the committee. The minority view may be valid but it may not be pursued for being singled out. The minority may not give their view because of a fear that if their solution proves wrong then they will be blamed for it.
3. No Accountability:
If these decisions are bad no individual accountability can be fixed . Every committee members tries to defend themselves by saying that he suggested a different solution. If accountability is not fixed then it is the weakness of the organisation.
4. Domination by Some Members:
In the committee meetings some members try to dominate. They try to put their view point on others. The aggressiveness of some members helps them to take majority with them and minority view is ignored. This type of decision making is not in the interest of the organisation.
5. Strained Relations:
Sometimes relations among committee members become strained. On certain issues if some members take divergent stands, some may feel offended. In case some issue concerning other persons is discussed in a committee and members taking stand not liked by those persons may offend them. The discussions in the meetings are generally leaked to other employees. Some unpleasant decisions may not be liked by those who are adversely affected. It affects relations of employees not only on the job but at personal level also.
6. Lack of Effectiveness:
In all areas the role of committees is not effective. Where grievance redressal or inter personal departmental matters are concerned the committees may be useful. where policies are to be framed and quick decisions are required committees may not be effective. Individual initiative will be more effective in these cases. So committees have a limited role to play.
Types of committees
1. Formal and Informal Committees:
Formal committee refers if a committee is formed as a part of organisation structure and is delegated some duties and authority. An informal committee may be formed to tackle some problem such as a manager may call some experts to help him in analyzing a problem and suggesting a suitable solution. The chief executive may call a meeting of departmental heads and some experts to find out a solution to some problem.
2. Advisory Committees:
These are the committees to advice line heads on certain issues. Line officers may discuss some problems to a committee for advice. The committee will collect information about the problem and recommend solution for the same. The suggestions of advisory committees can be accepted, modified or rejected by the line officers. These committees have no managerial powers and cannot apply their views on the line executives.
3. Line Committees:
There may be committees with managerial powers. Instead of giving a work to one person it may be assigned to a number of executives. The committees having administrative powers are called line or plural committees. Line committees help in planning company policies and programmes and organizing efforts at fulfillment of these plans, etc. For achieving organizational goals these committees also direct and control the activities of employees.
Key takeaways
- Committee means a body of persons entrusted with discharging some assigned functions as a group and in a corporate capacity.
- Committee is a group of persons pooling their thoughts and actions to facilitate the process of decision-making.
Meaning
A conference is a gathering of many people who talk about a specific subject or topic. People meet to confer about a theme. All the people have a common interest who attends the conference. It is not similar as a convention, which is typically much bigger and consists of delegates who represent various different groups.
Conferences are held on a large scale. People come to attend conferences from different fields of life, business, society, and religion, etc. to discuss a particular subject. They are formal affairs where invites are sent in advance, and a particular agenda has to be discussed and focused upon. The discussions, the topics are all prioritized in advance.
Participants in conference
- Businessman
- IT Professional
- Conservators
- Journalist
- Educators
- Students
- Authors
Points to be considered when planning a conference
- The purpose of the conference must be clearly understood
- The budget needs to be defined
- Meticulous planning must be carried out well in advance
- A back up plan to handle emergencies is always mandatory
- Planning works better when individuals in the planning and administrative committee have clear roles and responsibilities assigned
Essentials
Relevant content
The right content is presented to the audiences. Keep everyone in the loop on business aims and goals, the core message can often be summed up more quickly and easily. Keep it short to ensure that everyone takes it in; you can always recap in follow-up notes or emails.
Engaging activities
Our bodies are not designed to sit down for hours at a time, and after a while even the most keen listeners will inevitably find themselves zoning out. Thus try to limit talks to under an hour with plenty of breaks for people to get up for some fresh air. Or swap some of the presentations for activities that people can join in with- you can still get the same information.
Efficient planning
At an ideal conference, attendees should know what they are doing and when, each part of the day should start on time and there should be no waiting around. Employing a professional conference host to arrange the event and run it on the day will help to make sure that everything goes to plan.
A suitable location
The right location can really make the conference effective. If you are organising an event for a large team then hotels and other conference facilities can be useful. Try a beautiful historical building, relaxing outdoor space or inspiring sports venue to create a memorable backdrop for attendees.
The chance to have some fun
Conferences don’t have to consist of sitting in the same room listening to different presentations. Add some fun team building activities to get everyone involved.
Importance
Conference is the coming together of individuals who belong to a particular field. These individuals are invited to look at a particular matter in greater detail and communicate their view points and disseminate information among people belonging to that particular field.
Conferences could be held for a variety of reasons. They could be organized to raise general public awareness, or within the organization to study a particular problem, or to update the knowledge of the employees regarding the latest developments in the organization.
Difference between committee and conference
While a committee, as well as a conference, is a type of group communication, in a committee meeting the number of members is small, there is a well defined agenda and decisions taken are legally binding on the organization. A committee meeting is therefore a very formal affair, as its members are appointed, or nominated, and the meeting is organized with a view to solving a pertinent problem, or to implement a decision.
A conference, on the other hand, is a relatively informal get-together of a larger group that meets in an informal manner; the decisions taken at a conference are of a consultative or advisory nature. Participants in a conference do not have any voting right. In a conference, a given problem/ subject is analyzed from all angles in order to arrive at the best possible solution / option. These decisions are put forward in a recommendatory fashion.
Key takeaways
- A conference is a gathering of many people who talk about a specific subject or topic
- A conference is a meeting for consultation, discussion, or an interchange of opinions or views.
Reference-
- Lesikar, R.V. & Flatley, M.E.; Basic Business Communication Skills for Empowering the
Internet Generation, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Company Ltd. New Delhi. - Bovee, and Thill, Business Communication Today, Pearson Education
- Shirley Taylor, Communication for Business, Pearson Education
- Locker and Kaczmarek, Business Communication: Building Critical Skills, TMH
- Chhabra T.N, Effective Business Communication, Sun India Publications