UNIT 3
BASIC CONCEPTS OF DRAWING SOFTWARE
Manufacturing of a product is the main activity in engineering profession. The design of a product may start with trial designs in the form of sketches on paper. As the design improves and undergoes changes, the final form of design must be the scaled manufacturing drawings with finer details included. These drawings are two-dimensional representations of three-dimensional objects designed.
During the process of design, the designer may have to carry out a large amount of computations so that an optimum design is obtained. A computer with good graphic capabilities helps the designer to,
- Realize his ideas.
- Carry out complex computations.
- Present the results of computations in a useful form for decision making and possible improvement.
- Present the improved model for evaluation. Interactive Computer Graphics (ICG) is the tool of the designer.
Merits of CAD
- Saves time: When you are using the computer-aided design software, it will save your time and you can make better and more efficient designs in shorter time duration.
2. Easy to edit: When you are making designs, you may find the need to make alterations. When you are using computer-aided design software, it will be much easier to make any changes because you can fix the errors and modify the drawings easily.
3. Decrease in error percentage: As the CAD software makes use of some of the best tools, the percentage of error that occurred because of manual designing is significantly reduced.
4. Decrease design effort: When it comes to the amount of effort that was needed for the sake of designing the different models, it has been reduced significantly because the software automates most of the task.
5. Code re-use: As the entire task is carried out with the help of computer tools, it removes the problem of duplication of labor, you can copy the different parts of code and design which can then be reused multiple times over and over again.
6. Easy to share: The CAD tools make it easier to save the files and store it in a way that you can use it time and again and send it without any unwanted hassles too.
7. Improved accuracy: There is absolutely no doubt about the fact that the kind of accuracy that CAD software will offer can never be achieved by opting for manual drawings. You have tools to measure the precision, skill and accuracy level of the designs.
Demerits of CAD:
- Work can be lost because of the sudden breakdown of computers
- Work is prone to viruses
- Work could be easily “hacked”
- Time taking process to know how to operate or run the software
- High production or purchasing cost for new systems
- Time and cost of training the staff which will work on it
- Need of regular updating of software or operating systems
- Needs less employment because of CAD/CAM systems
The CAD system creates an environment to prepare drawings interactively. Most CAD systems available commercially are menu driven. Commands can either be typed directly with the help of a keyboard or can be picked-up from the screen menu or from tool bar with the help of a mouse or can be selected from the digitizer menu. Some screen menus offer pull-down menus (also referred to as pop-up menus) and dialogue boxes.
For example, a variety of hatching patterns are displayed on the screen for better visualization and selection if a hatching command is chosen. The appropriate hatching pattern can be selected with the help of input device. The effect of every command immediately displayed on the screen so that selection and corrections can be done interactively and immediately.
The major functions to be performed by a computer aided drafting system are:
(a) Basic set-up of a drawing
(b) Drawing the objects
(c) Changing the object properties
(d) Translating the objects
(e) Scaling the objects
(f) Clipping the objects to fit the image to the screen
(g) Creating symbol libraries for frequently used objects
(h) Text insertion
(i)Dimensioning
(j)Creates various layers (Transparent sheets)
(k) Allows zoom-in and zoom-out of any components drawing
(I) Creates different numbers of print/plot layouts.
A GUI (graphical user interface) is a system of interactive visual components for computer software. A GUI displays objects that convey information, and represent actions that can be taken by the user. The objects change color, size, or visibility when the user interacts with them.
GUI objects include icons, cursors, and buttons. These graphical elements are sometimes enhanced with sounds, or visual effects like transparency and drop shadows.
A GUI is considered to be more user-friendly than a text-based command-line interface, such as MS-DOS, or the shell of Unix-like operating systems.
LIMITS
- The Limits command in AutoCAD is used to set an invisible rectangular boundary in the drawing area or viewport. It limits the grid display and the point locations.
- We are required to specify the coordinates of the opposite corners of the rectangular window. The opposite corners are named as Upper right and Lower left corners.
Steps to set the limits
The steps to set the limits are listed below:
- Open the AutoCAD software.
- Type LIMITS on the command line or command prompt.
- Press Enter or spacebar.
- Write the coordinates of the lower-left corner. For example, (0,0). The coordinates for the lower-left are usually the coordinates of origin for better understanding. We can also modify the coordinates according to the requirements.
- Press Enter.
- Write the coordinates of the upper-right corner. For example, (200, 200).
- Press Enter.
- Write Z. Here Z signifies Zoom.
- Press Enter.
- Write E. Here, E signifies Extend.
- Press Enter.
Example 1:
Draw a rectangle of dimension 100 x 200.
Here, the length of the rectangle is 100, and the width is 200.
The steps are listed below:
- Type LIMITS on the command line or command prompt.
- Press Enter.
- Write the coordinates of the lower-left corner (0, 0).
- Press Enter.
- Write the coordinates of the upper-right corner (300, 400). You can also increase the limits according to your choice.
- Press Enter.
- Write Z. Here Z signifies Zoom.
- Press Enter.
- Write E. Here, E signifies Extend.
- Press Enter.
- Type Rec or Rectangle on the command line.
- Press Enter.
- Specify the first corner point on the viewport.
- Specify the length and breadth of the rectangle in the form of @length, width. For example, @100,200
- Press Enter.
Using above steps, the rectangle will be created.
UNITS
Use this procedure to specify the drawing units in a new or existing drawing.
If you change the drawing units, you can specify whether existing objects in the drawing are scaled to the new units or retain their original size. You can also specify whether objects inserted from a drawing that uses different units are scaled to the units in the current drawing, or retain their original size.
You can specify the unit type and precision for linear, angular, area, and volume units. The precision values specify only the number of decimal places displayed in the interface. They do not determine the number of decimal places used in the software to make calculations.
When you change the drawing units, the default options under Area and Volume change to reflect the new drawing units. The drawing scale options on the Scale tab also change to reflect the new drawing units.
- Click

 Utilities
Utilities Drawing Setup.
Drawing Setup.
- Under Drawing Units, select the desired units.
Various imperial and metric units are available. The units that you select determine the unit of measurement that each unit in your drawing represents. For example, if you select Inches, each drawing unit equals one inch.
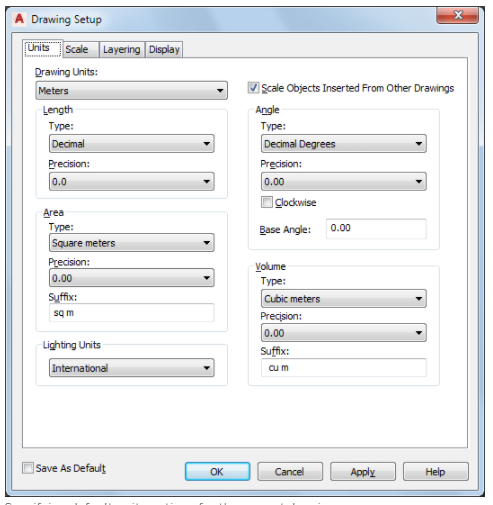
2. To scale objects that you insert into the current drawing from drawings with different drawing units, select Scale Objects Inserted from Other Drawings.
Clear this option to insert objects at their original size without scaling. For example, if an item that is one inch long were inserted into a drawing set to millimeters, this setting would scale the item to 25.4 mm in length when enabled. With this setting disabled, it would remain one unit long (which would now be only one millimeter rather than one inch).
3. Under Length, select a unit type and desired precision.
4. Under Angle, select an angle type and desired precision.
If you want to measure angles clockwise instead of counterclockwise, select Clockwise.
5. Under Base Angle, enter a value for the default 0 angle direction. The default is 0 degrees (East) and a counter-clockwise direction.
Imported survey drawings may include drafting instructions where changing the base angle might be desirable to properly orient the data.
Every point in an AutoCAD drawing file can be identified by its X,Y,Z coordinates. (In most 2D drawings, the Z-coordinate value is 0.0.) This system of coordinates is referred to in AutoCAD as the world coordinate system
To work in AutoCAD is necessary to know the Coordinate System
When we draw a line or any character or point, the start position will be set in relation to the coordinate system.
Coordinate system understand as a plane that can be in a position if it is a 2D drawing or more positions when it comes to drawing in 3D.
So we start from starting point in relation to the axis X and Y coordinates with the position we are in a certain place (more about that below), but remember the word origins, to the position which is currently located prior to drawing. Each time when we are positioned somewhere, our starting point is the starting point no matter where in the drawing are. The position of the origin depends on the draw in the absolute or polar coordinate system (although we may in the course of combined systems that we want).
Short explanation coordinate system.
Our starting point is always in the direction East and to the first X followed by Y coordinates in direction North. (x,y).
So our starting point is the central starting point. When the Command line write some coordinates, AutoCAD will be based on this starting point (which is currently on the drawing) in relation to his position will be the starting point drawing.
Used as a guide to X axis first coordinate and Y axis for the second coordinate (except in Cartography Geodesy, there are reversed coordinates - replaced, what is the X axis in mechanical engineering and construction to the Y axis in
geodesy). It is also important to note that the axis X and Y can be so negative compared to the starting point for some sort of starting point we can enter a drawing and negative coordinate.
These negative coordinates positioned in Quadrant II and III for the X axis, and III and IV quadrant of the Y axis.
SNAP
Function button Snap, on/off option which we determine what will be the support network that is a step that will move the cursor on the drawing. Here note, if you cannot click the mouse pointer exactly to a specific location on a drawing, but you always Autocad positioned closest to a town then you SNAP included a big step. Simply turn off SNAP click of a button.
In the picture below you see that you can set up as desired by the X axis and Y axis (in the picture is 10 units of the spacing between neighboring points), it turns on and off with the (F9).
GRID
Also note that on the same card can be On/Off GRID (F7)
ORTHO
Orthogonal drawing or rectangular drawing, it means that when you turn this feature lines that you drag the mouse will be angled in relation to the UCS and you can draw only the angle that is set and it is 90 degrees.
POLAR
Polar coordinates follow when you draw the line, if this function is activated then the Ortho automatically turned off because when you draw with the POLAR function of the mouse you can draw lines at an angle to the set and you can also set up and draw it with absolute or relative coordinates when drawing lines.
OTRACK
F11 - Intersection, Perpendicular, Tangent, Nearest, Apparent intersection, Parallel
If you turn OTRACK/POLAR mode then you have an active extra dashed line that helps you draw the line to align with a line (point) to the already drawn parts of the drawings.
BLOCK
In AutoCAD, a block is a collection of objects that are combined into a single named object. The following are some sample blocks at various scales.
Some of these blocks are realistic representations of objects, some are symbols, and one of them is an architectural title block for a D-size drawing.
Blocks also help you in keeping the file size under control. A drawing made with blocks for repetitive objects will be far smaller than the drawing which uses copied instances of repetitive objects.
Blocks also help in keeping consistency in your project drawings, by using the same set of blocks you can avoid a lot of confusion among different members working on a project.
VIEWPORTS
Layout viewports are objects that display views of model space. You create, scale, and place them in paper space on a layout.
On each layout, you can create one or more layout viewports. Each layout viewport is like a closed circuit TV monitor of a view of the model at a scale and orientation that you specify.
LAYER
Layers are the primary method for organizing the objects in a drawing by function or purpose. Layers can reduce the visual complexity of a drawing and improve display performance by hiding information that you don’t need to see at the moment.
Before you start drawing, create a set of layers that are useful to your work. In a house plan, you might create layers for the foundation, floor plan, doors, fixtures, electrical, and so on.